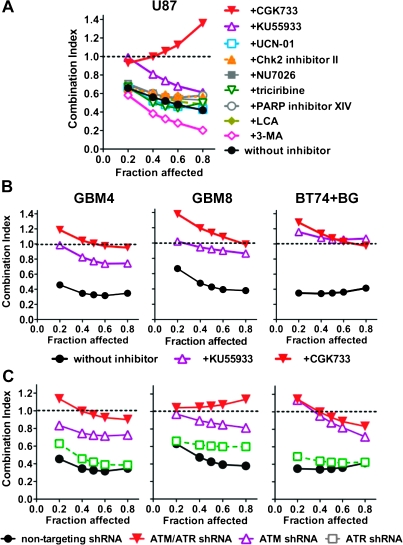
Figure 3.
Effect of inhibition of DNA damage response pathways on synergy. A) U87 cells were treated with pharmacological inhibitors of DDR pathways at the concentrations indicated in Supplementary Table 1 (available online), and the interactions between TMZ and G47Δ analyzed. Data are shown as Fraction affected–Combination Index (CI) plot. B) Interaction between G47Δ and TMZ in GSCs (GBM4, GBM8, and BT74 [pretreated with 50 μM BG]) treated with ATM inhibitors CGK733 (5 μM) or KU55933 (20 μM). C) Interaction between G47Δ and TMZ in GSCs (GBM4, GBM8, and BT74 [pretreated with 50 μM BG]) lentivirally transduced with shRNA targeting ATM, ATR, ATM + ATR, or nontargeting shRNA. CI < 1, CI = 1, and CI > 1 represent synergistic, additive, and antagonistic interactions, respectively. The experiments were repeated at least three times for each of the conditions, each time in triplicate. ATM = ataxia telangiectasia mutated; ATR = ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related; BG = O6-benzylguanine; CGK733 = ATM/ ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) kinase inhibitor; Chk2 = checkpoint kinase 2; DDR = DNA damage response; GSCs = glioblastoma stem cells; KU55933 = activated ATM kinase inhibitor; LCA = lithocholic acid; NU7026 = DNA-dependent protein kinase inhibitor; PARP = poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase; shRNA = short-hairpin RNA; TMZ = temozolomide; UCN-01 = cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor; 3-MA = autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine.