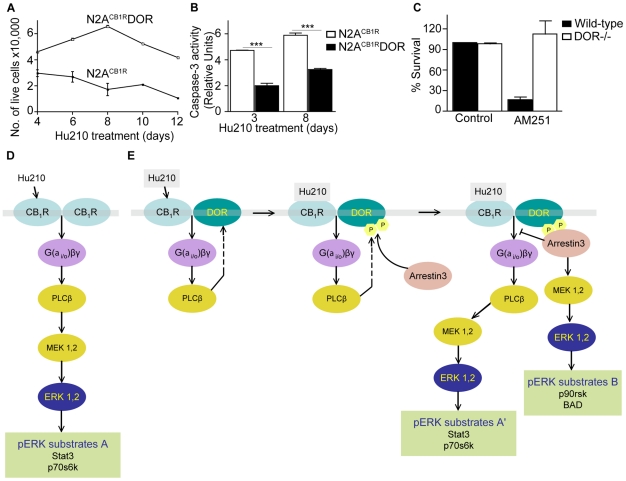
Figure 6. CB1R-DOR heteromerization promotes cell survival.
A, Hu210-treated N2ACB1RDOR cells exhibit increased survival compared to N2ACB1R cells. N2ACB1R or N2ACB1RDOR cells were treated with 1 µM Hu210 for the indicated days and survival measured by trypan blue exclusion as described in Methods. Data represent Mean ± SEM (n = 4 in triplicate). B, Hu210-treated N2ACB1RDOR cells exhibit lower apoptosis as compared to N2ACB1R cells. Apoptosis of N2ACB1R or N2ACB1RDOR treated for 3 or 8 days with 1 µM Hu210 was measured using caspase-3 activity assay as described in Methods. Data represent Mean ± SEM (n = 4 in triplicate); ***p<0.001 N2ACB1RDOR vs N2ACB1R (t test). C, CB1R antagonist treatment decreases neuronal survival of striatal neurons from wild-type but not DOR−/− mice. Primary striatal neurons from wild-type or from DOR−/− mice were prepared as described in Methods. The CB1R antagonist AM251 (10 µM) was added to the growth media at DIV7 and cellular viability assessed at DIV10 as described in Methods. Data represent Mean ± SEM (n = 2–4) D–E, A schematic of the signaling pathways emanating from CB1R in N2ACB1R (D) and N2ACB1RDOR (E) cells. Activation of CB1R in N2ACB1RDOR cells leads to differential activation of signaling molecules and phosphorylation of ERK substrates.