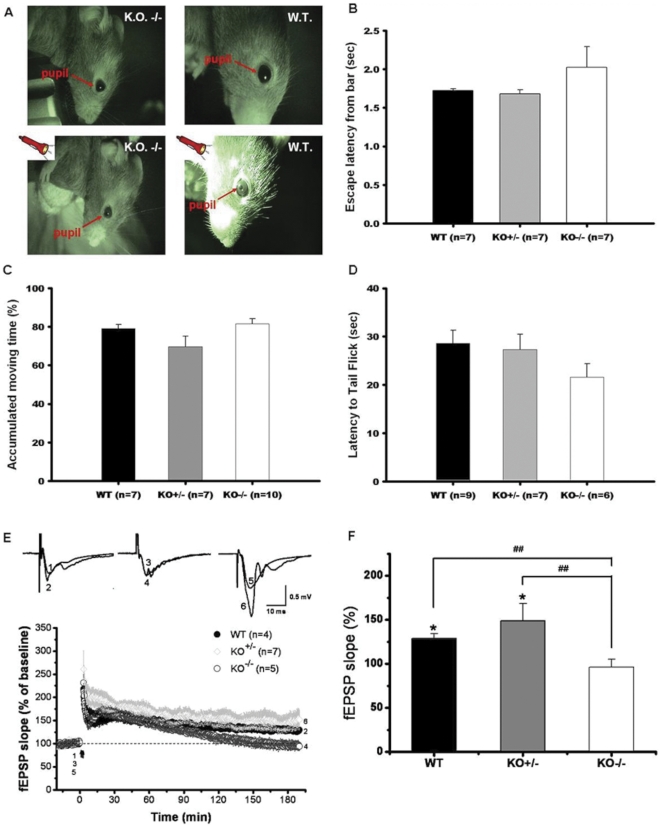
Figure 1. Characterization of the Cav3.2 −/− mice.
A. Reaction to light. The reaction of the mice to light was examined by shining a bright light in the eyes and looking for the pupillary reflex. The mice were placed in a dark room for 15 minutes prior to test. The pupillary reflex of the WT and Cav3.2 −/− mice were similar. B. Visual perception test. The escape latency of the WT, Cav3.2 +/− and Cav3.2 −/− mice were similar when the bar was inserted to a dark chamber. Three strains stayed away from the bar and looked at it when it moved around in the air. C. Locomotor activity. During the first 2 minutes of baseline and before the onset of the first tone-shock trace fear conditioning, accumulated moving times were similar among the WT, heterozygous knock-out and homozygous knock-out mice. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of animals used in the experiment. D. Nociception test. No significant difference was observed between the three groups of mice. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of animals used in this test. (WT: wild-type; KO +/−: Cav3.2 +/−; KO −/−: Cav3.2 −/−) E. LTP induced at CA1 synapse in slices from WT, Cav3.2 −/− and Cav3.2 +/− mice. Time course of LTP induced with high frequency stimulation. Note no significant differences in post-tetanus potentiation or expression of early LTP were found among the three groups. F . Bar chart showing significant differences in expression of L-LTP between WT, Cav3.2 −/− and Cav3.2 +/− mice. LTP values in WT, Cav3.2 −/− and Cav3.2 +/− mice were 128.9±5.5%, 96.3±9.1%, 149±19.5% of baseline, respectively. # # indicates p<0.01.