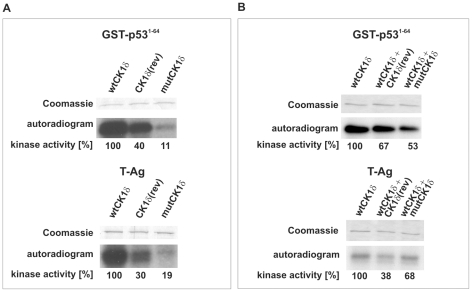
Figure 4. Phosphorylation of GST-p531–64 and baculovirus-expressed T-Ag by GST-CK1δ(rev) and GST-mutCK1δ.
(A) Phosphorylation of GST-p531–64 and baculovirus-expressed T-Ag by GST-wtCK1δ, GST-CK1δ(rev) or GST-mutCK1δ. In vitro kinase assays were performed using GST-p531–64 (FP267) or baculovirus-expressed T-Ag as substrates and GST-wtCK1δ, GST-CK1δ(rev) or GST-mutCK1δ as enzyme. The phosphorylated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (12.5%) and visualized by Coomassie staining. The degree of phosphorylation was documented by autoradiography as well as Cherenkov counting. (B) Phosphorylation of GST-p531–64 or baculovirus-expressed T-Ag by mixed GST-wtCK1δ and GST-CK1δ(rev) or GST-mutCK1δ. In vitro kinases assays were performed using GST-p531–64 (FP267) or baculovirus-expressed T-Ag as substrates and GST-wtCK1δ in combination with equal amounts of either GST-CK1δ(rev) or GST-mutCK1δ as enzyme. In a control reaction, same amounts of GST-wtCK1δ were used diluted in kinase buffer. The phosphorylated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (12.5%) and visualized by Coomassie staining. The degree of phosphorylation was documented by autoradiography and by Cherenkov counting and is presented in % activity.