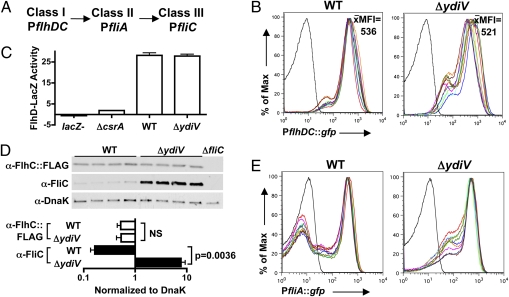
Fig. 3.
YdiV controls the heterogeneity of fliA (σ28) transcription. (A) The Salmonella flagellar gene regulatory cascade. (B) YdiV does not repress flhDC transcription. The average MFI of 10 independent trials per strain is reported. The black line represents GFP-negative control. (C) A lacZ translational reporter fusion to flhD reveals that YdiV does not repress the translation of class I proteins. csrA is required for efficient translation of the flhDC mRNA (32); thus, a ΔcsrA mutant serves as a negative control. (D) Western blot analysis demonstrates that WT and ΔydiV Salmonella contain similar amounts of FlhC protein. Four independent samples of each strain are shown. FlhC and FliC expression were normalized to the DnaK loading control for quantification. The ΔfliC mutant does not harbor the FlhC::3× FLAG construct. (E) YdiV represses fliA transcription. The black line represents GFP-negative control. All experiments were performed using exponential-phase cultures.