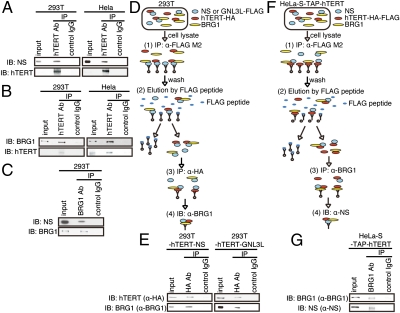
Fig. 5.
NS forms a complex with hTERT and BRG1. (A) hTERT interacts with endogenous NS. hTERT complexes from 293T or HeLa cells were purified with an anti-hTERT antibody (Rockland), and associated proteins were subjected to SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with an anti-NS antibody. IB, immunoblot. (B) hTERT interacts with endogenous BRG1. hTERT immune complexes from 293T or HeLa cells were subjected to SDS/PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with an anti-BRG1 antibody. (C) BRG1 interacts with endogenous NS. BRG1 complexes from 293T cells were purified by immunoprecipitation with an anti-BRG1 antibody and subjected to SDS/PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with an anti-NS antibody. Schema (D) and results (E) of the sequential immunoprecipitation using cells expressing FLAG-tagged NS or GNL3L and hTERT-HA. NS or GNL3L immune complexes were isolated and then eluted with the FLAG M2 peptide. hTERT immune complexes were then purified, and endogenous BRG1 was detected by immunoblotting. Schema (F) and results (G) of the sequential immunoprecipitation using cells stably expressing TAP-hTERT. hTERT immune complexes were isolated and eluted with the FLAG M2 peptide. Endogenous BRG1 immune complexes were isolated, and endogenous NS was analyzed by immunoblotting.