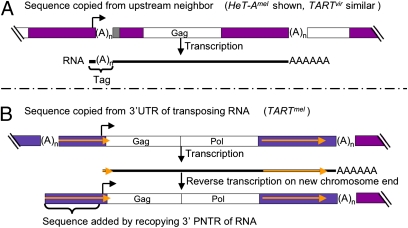
Fig. 3.
Mechanisms for adding buffering 5′ sequence. (A) Sequence copied from upstream neighbor. Used by HeT-Amel and TARTvir. Telomere segment with a complete HeT-Amel flanked by other HeT-As. Transcription starts at the bent arrow in the upstream element and continues through the complete element. The resulting RNA (black line) has a Tag of the last nucleotides of the upstream element. On transposition, this Tag will become the 5′ end of the new element, undergo erosion, and if transposed again, be internalized into the string of variably eroded Tags indicated by the gray box at the 5′ end of the complete element. (B) Sequence copied from the 3′ UTR of transposing RNA. Used by TARTmel. Telomere segment with a complete TARTmel flanked by distal TART and proximal HeT-A. (A)n, 3′ oligoA in DNA; AAAAAA, polyA tail on RNA; gold arrows, PNTRs; other annotation as in Fig. 1. Transcription starts at the bent arrow and produces RNA with a very short 5′ UTR. When this is reverse-transcribed onto the chromosome end, the RT jumps back to the 3′ UTR and copies sequence to extend the 5′ UTR (Fig. 4).