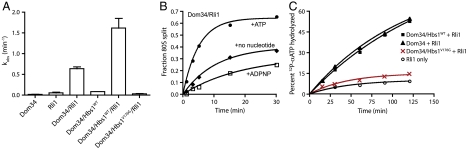
Fig. 2.
Dom34∶Hbs1∶Rli1-facilitated subunit dissociation and its nucleotide dependence. (A) Observed rate constants for subunit dissociation in the presence of Dom34, Rli1, and/or Hbs1 and its derivatives. The reported rate constants were determined by monitoring the formation of free peptidyl-tRNA in a native gel system (n≥3, ± SEM). (B) Rli1-mediated subunit dissociation is dependent on ATP hydrolysis. Subunit splitting was monitored by peptidyl-tRNA formation in the presence of Dom34 and Rli1 with or without various nucleotides. (C) Multiple-turnover ATP hydrolysis by Rli1 on empty 80S ribosomes complexed with various factors, as indicated. The fraction of radiolabeled ATP that was hydrolyzed at each time point was monitored by thin-layer chromatography similar to Fig. 1B.