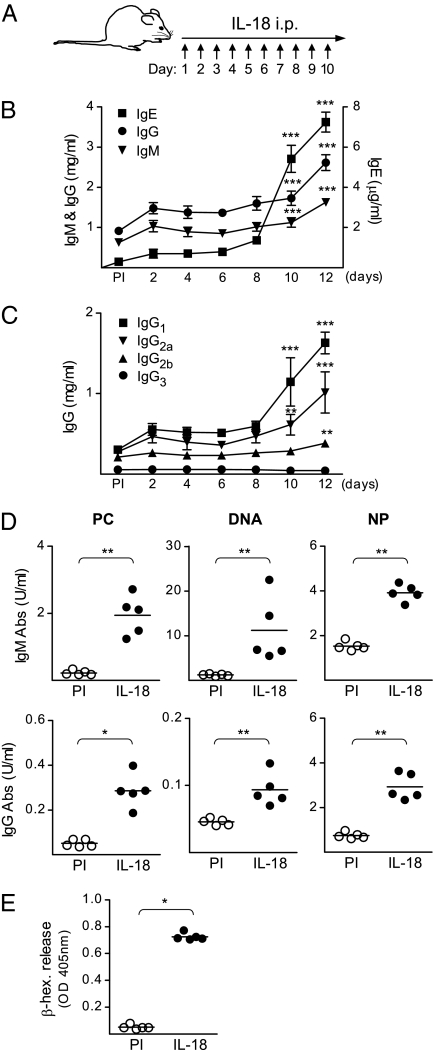
Fig. 1.
The levels of total IgM, IgG, and IgE as well as innate antibodies increase in serum of IL-18–injected mice. (A) Schematic outline of the IL-18 injections in WT (129/SvEv) mice. (B and C) Serum levels of (B) total IgM, IgG, and IgE and (C) total IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG3 in IL-18–injected mice. Mean and SEM from 5 to 25 mice per group [preimmune (PI) and indicated time points] are plotted. (D) Serum levels of IgM and IgG reactive with PC, DNA, and NP in IL-18–injected mice. Mean and individual mice (PI and day 12) are plotted. (E) The increased IgE levels in IL-18–injected mice induce mast cell degranulation. β-Hexosaminidase (β-hex) released from BMMCs incubated with sera from untreated or IL-18–injected mice, followed by anti-IgE cross-linking. Mean and individual mice (PI and day 12) are plotted. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by comparing IL-18–injected mice to the PI group with a Mann–Whitney test.