Fig. 3.
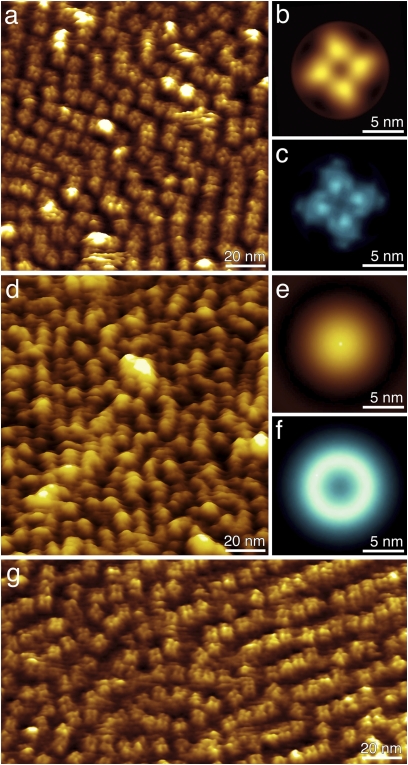
High-resolution AFM topographs of the R348A mutant cyclic nucleotide-regulated potassium channel MlotiK1. (A) Mutant potassium channels imaged in the presence of cAMP. Single MlotiK1 tetramers protrude 3.1 ± 0.5 nm (n = 57) from the lipid bilayer. (B and C) Correlation average (B) and SD map (C) of 73 MlotiK1 tetramers showing details of the CNB domains. (D) Mutant potassium channels imaged in the absence of cAMP. The topograph shows single protrusions that correspond to individual MlotiK1 tetramers and extend 4.9 ± 0.6 nm (n = 148) from the lipid bilayer. (E) Single-particle average of 256 protrusions. (F) SD map of E showing the high structural variability of the protrusions in the unbound state. (G) Mutant Mlotik1 imaged after readdition of cAMP shows single tetramers that protrude 3.2 ± 0.5 nm (n = 45) from the lipid bilayer. AFM topographs have full-color levels corresponding to vertical height scales of 4 nm (A, B, and G), 0.6 nm (C), 6 nm (D and E) and 1.5 nm (F). Imaging buffer was 50 mM KCl, 900 μM cAMP (A and G), no cAMP (D), and 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5).