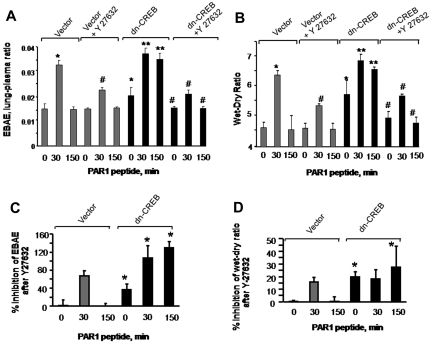
Figure 7.
Inhibition of RhoA signaling restores endothelial barrier function in dn-CREB lungs. Mice transducing control vector or dn-CREB mutant were given with either normal saline (vehicle) or Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (10 mg/kg body weight mice) intravenously for 15 minutes. Mice were then injected with either control peptide or PAR1 peptide for the indicated times. Evans blue was injected into the mice 30 minutes before they were euthanized. Lung vascular permeability measurements were determined by quantifying transendothelial albumin flux of EBA (A) or lung wet-dry ratio (B). Data represent mean ± SEM from 3 individual experiments. Asterisk (*) indicates values different from control vector group at 0 time point, and double asterisk (**) indicates values different from values in corresponding PAR1 peptide–treated control group (P < .05). Pound (#) indicates values different from dn-CREB mutant lungs (P < .05). (C-D) Mean + SD of percentage of change in inhibition of lung vascular permeability (C) and lung wet-dry weight ratio (D) by Y-27632. Values shown in panels A and B were recalculated taking time 0 value in vector-expressing lungs as 100%. Asterisk (*) indicates values different from control vector group.