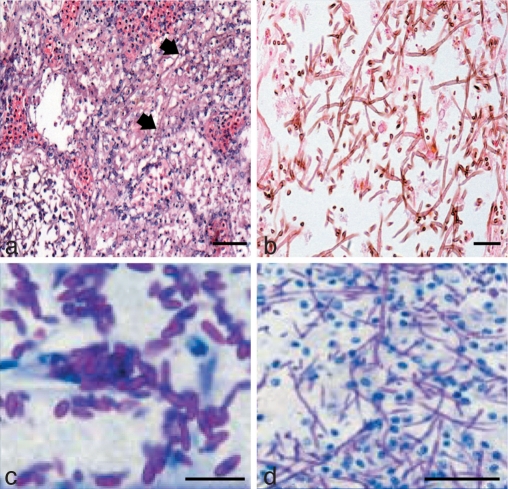
Fig. 16.
Examples of histopathology of Exophiala species. – a, b. Disseminated phaeohyphomycosis by E. aquamarina in weedy seadragons (Phyllopteryx taeniolatus); a. abundant brown fungal hyphae (arrows) coursing through necrotic tubules, interstitium, and sinusoids in renal parenchyma. Stained with H & E. Reproduced from Nyaoke et al. 2009; b. fungal hyphae, kidney; weedy seadragon. Hyphae are slender, filamentous, and septate with occasional right-angled branches. Fontana-Masson staining; walls of hyphae stain brown, indicative of melanin. Reproduced from Nyaoke et al. 2009. – c. Light micrograph of transverse section of a gill of lethargic mangrove crab (Ucides cordatus) lamella with numerous conidia of E. cancerae in lacunae. Stained with PAS. Reproduced from Boeger et al. 2005. – d. Light micrograph of cardiac tissue of lethargic mangrove crab (Ucides cordatus) parasitized by hyphae of E. cancerae. Stained with PAS and counter-stained with H & E. Reproduced from Boeger et al. 2005. — Scale bars: a, d = 50 μm; b = 25 μm; c = 15 μm.