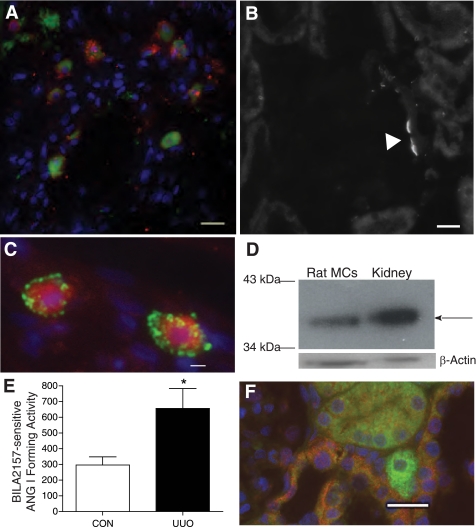
Fig. 4.
Rat kidney mast cells express renin. A: control kidney mast cells constitutively express renin. Shown is staining of connective tissue mast cells in rat kidney with FITC-conjugated avidin (green) and a polyclonal anti-renin antibody conjugated to Alexa Fluor 594 (red). The staining is not colocalized. Scale bar = 10 μm. B: the polyclonal anti-renin antibody exhibits specific binding to rat kidney at the vascular pole of the glomerulus. Scale bar = 10 μm. C: mast cells are immunopositive for renin. Shown is staining of mast cells in UUO rat kidney (14 day) with rhodamine-conjugated avidin (red) and a FITC-conjugated polyclonal anti-renin antibody (green). The staining is not colocalized. Scale bar = 10 μm. D: Western blot probing rat kidney mast cells (20 μg/lane) and rat kidney tissue for renin with the polyclonal anti-renin antibody. The arrow shows the ≈35-kDa band for renin. β-Actin expression was used as a loading control. E: ANG I formed (BILA2157-sensitive renin activity in pg·ml−1·min−1) as measured in lysates from mast cells isolated from 14-day UUO and CON kidneys [657 ± 126 pg·ml−1·min−1 UUO (n = 3) vs. 297 ± 51 pg·ml−1·min−1 CON (n = 3)]. Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05. F: (pro)renin receptor immunoexpression in UUO rat kidney. Shown are representative images of kidney sections incubated with anti-(pro)renin receptor antibody conjugated to Alexa Fluor 594 (red) and avidin-FITC (green) to identify mast cells. (Pro)renin receptor expression is seen in the distal tubules (red) but is not expressed in the avidin-labeled degranulating mast cell (green) shown in the image. Nuclei were counterstained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Scale bar = 20 μm.