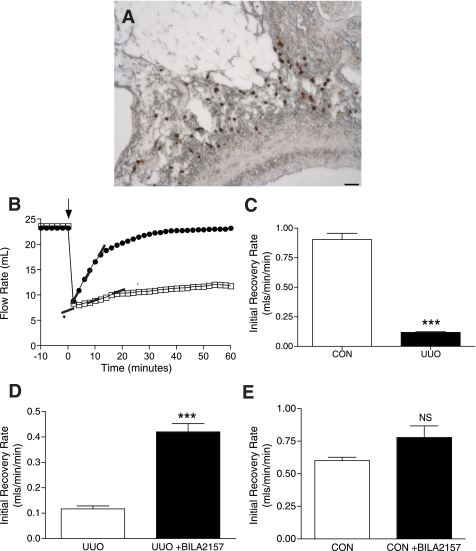
Fig. 6.
Mast cell renin release increases vascular resistance in isolated, perfused UUO rat kidney. A: mast cells, labeled with avidin-HRP (brown), are closely apposed to renal artery in rat kidney. Scale bar = 50 μm. B: UUO kidney (14 day) has a slower initial rate of flow recovery after an acute increase in vascular resistance compared with CON kidney as shown in the representative traces of the flow rate response [UUO (□) and CON (○)]. Initial rates of flow recovery, as indicated by the dashed lines, are 0.13 ml·min−1·min−1 for UUO kidney and 0.85 ml·min−1·min−1 for CON kidney. C: initial flow recovery rate is significantly impaired in UUO compared with CON kidneys [0.12 ± 0.01 ml·min−1·min−1 UUO (n = 4) vs. 0.91 ± 0.05 ml·min−1·min−1 CON (n = 4)]. Values are means ± SE. ***P < 0.001. D: BILA2157-treated UUO kidney shows an improved initial rate of flow recovery compared with untreated UUO kidney [0.42 ± 0.03 ml·min−1·min−1 +BILA2157 (n = 4) vs. 0.12 ± 0.01 −BILA2157 (n = 4)]. Values are means ± SE. ***P < 0.001. E: BILA2157 treatment has no effect on the initial rate of flow recovery in CON kidney [0.78 ± 0.09 ml·min−1·min−1 +BILA2157 (n = 5) vs. 0.06 ± 0.03 −BILA2157 (n = 5)]. Values are means ± SE.