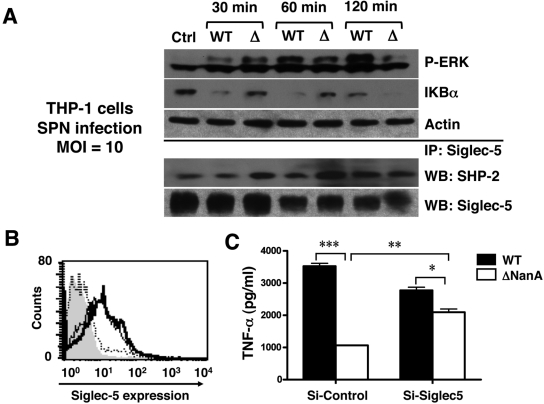
FIG 3 .
Signaling pathways implicated in macrophage inflammatory activation by S. pneumoniae NanA. (A) THP-1 cells were infected with WT S. pneumoniae or ΔNanA mutant at an MOI = 10. At the indicated times, cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for ERK1/2 phosphorylation and IκB degradation. SHP-2 recruitment to Siglec-5 was revealed by immunoprecipitating cell lyates with anti-Siglec-5 Ab, followed by probing with anti-SHP-2 Ab. (B) Knockdown of Siglec-5 expression by RNA interference. THP-1 cells were infected with lentiviruses carrying control shRNA (thin line) or Siglec-5 targeting shRNA (dashed line), and the knockdown efficiency was determined by FACS analysis with APC-conjugated anti-Siglec-5 MAb to measure cell surface Siglec-5 expression. THP-1 cells stained with APC-conjugated isotype MAb (solid gray) and anti-Siglec-5 MAb (thick line) served as negative and positive controls, respectively. (C) Control or Siglec-5 knockdown THP-1 cells were infected with WT S. pneumoniae or ΔNanA mutant at MOI = 10 for 3 h, and the culture supernatants were collected to determine TNF-α concentrations. Experiments were conducted twice with biological duplicates. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s posttest. ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.