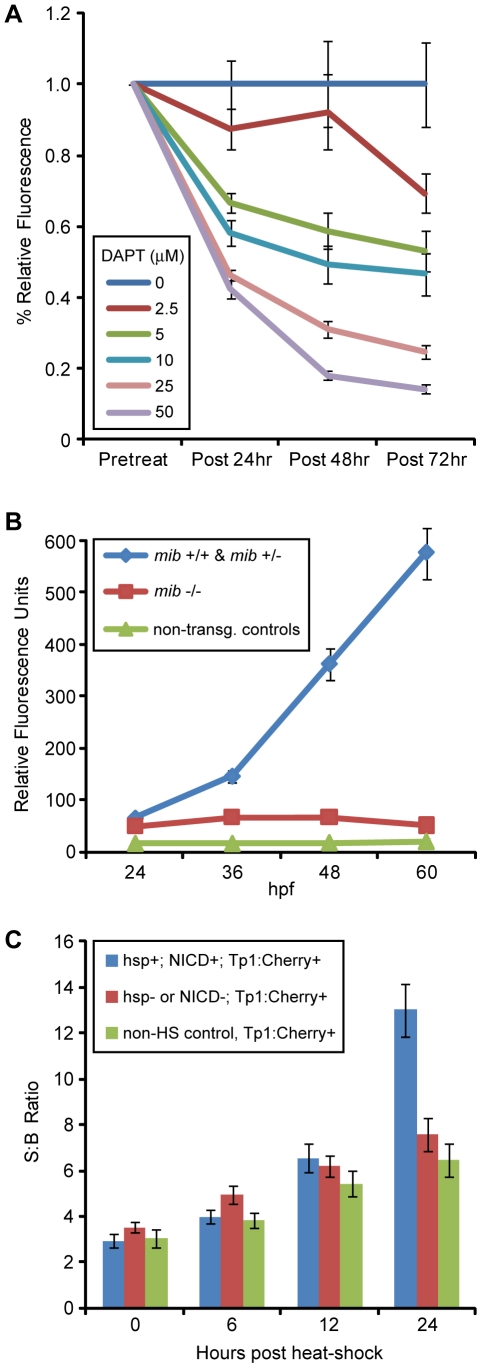
Figure 4. ARQiv detection of modulations in Notch pathway signaling.
A) Comparison of fluorescence levels in the Notch-signaling transgenic reporter line, Tp1:GFP treated with increasing concentrations of DAPT (an inhibitor of gamma-secretase proteolytic activity). Following pre-treatment scans at 48 hpf, DAPT treatments commenced and post-treatment scans were taken every 24 hrs thereafter until 120 hpf. The results show a concomitant decrease in Notch signaling with increasing DAPT concentration. Paired t-tests showed that all DAPT treatments of 5 µM and above are significantly different (p-value ≤0.05) than controls from post-24 hr onward. B) Comparison of fluorescence levels in Tp1:Cherry embryos within the context of the Notch pathway mutant mindbomb (mib). The mib mutation is believed to abrogate Notch-signaling by preventing normal function of the ligand Delta. Embryos from a mib/+; Tp1:Cherry incross were phenotypically screened at 24hpf to delineate mib (-/-), from wildtype (wt, +/+) and heterozygotes (het, +/-), as well as to identify non-transgenic siblings. Reporter expression levels were then quantified every 12 hrs thereafter until 60 hpf. The wt transgenic embryos show a steady increase in Notch reporter expression; however, the mib transgenic embryos show a constant low expression level near that of non-transgenic controls. Paired t-tests showed revealed the mib embryos produced significantly lower (p-value ≤0.05) reporter levels than wt and het siblings starting at 24 hpf. C) Comparison of fluorescence levels in Tp1:Cherry embryos within the context of Notch pathway activation following induction of NICD expression in Tp1:Cherry; hsp:Gal4; UAS:NICD triple transgenic larvae. Controls included both non-heat shocked Tp1:Cherry + siblings and heat-shocked Tp1:Cherry + siblings in which hsp:Gal4 and/or UAS:NICD was not present. Prior to heat shock a pre-treatment scan was performed at 4 dpf. An initial heat shock was performed to induce expression of NICD and repeated 12 hrs later. Scans were performed every 6 hrs over the next 24 hrs. Larvae with a slope of mCherry expression two standard deviations above non-heat shock controls were considered positive for all three transgenes and pooled. Larvae below this cut-off were considered to be negative for at least one of the other transgenes and pooled as heat-shocked negative controls. The data show that over-expression of NICD leads to a significant increase in expression of the mCherry reporter at 24 hours (p-value = 8.3E−06) post heat-shock in keeping with ligand-independent activation of the Notch pathway.