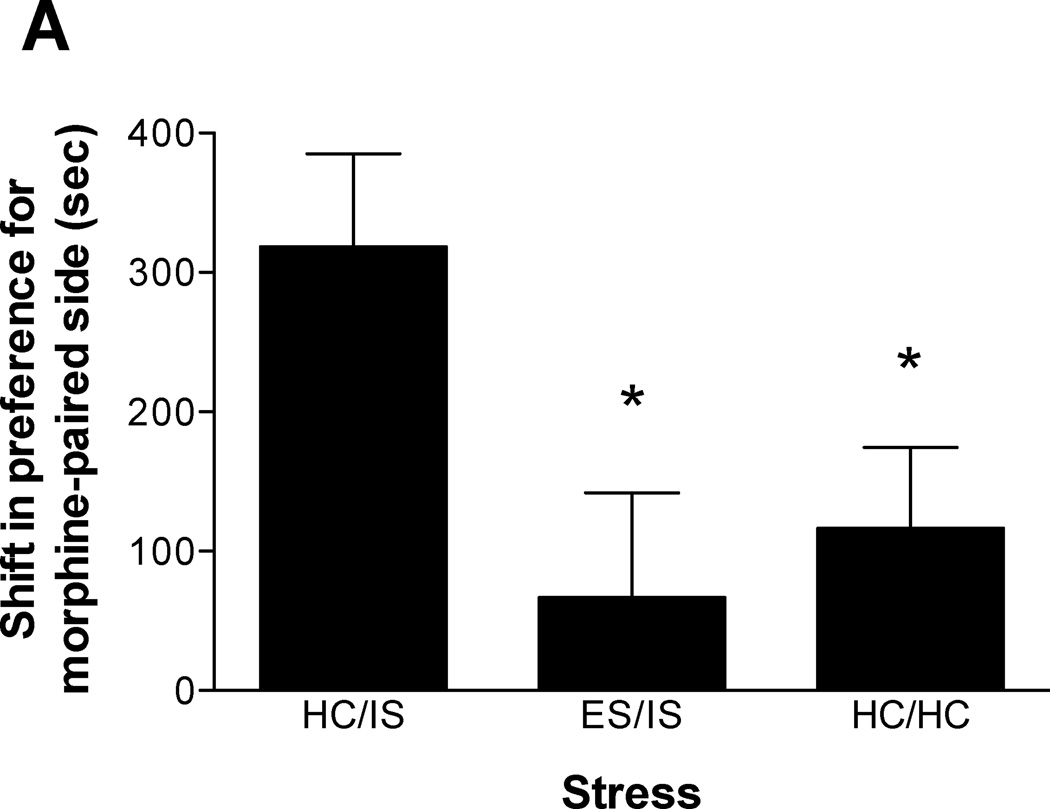
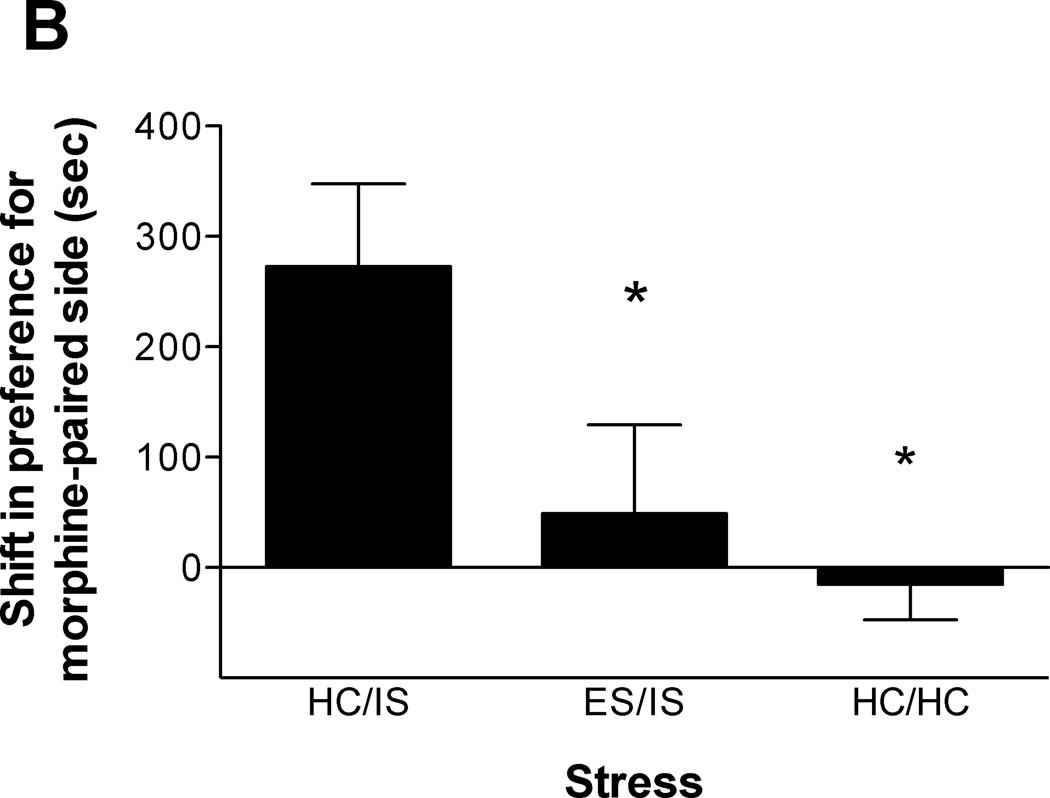
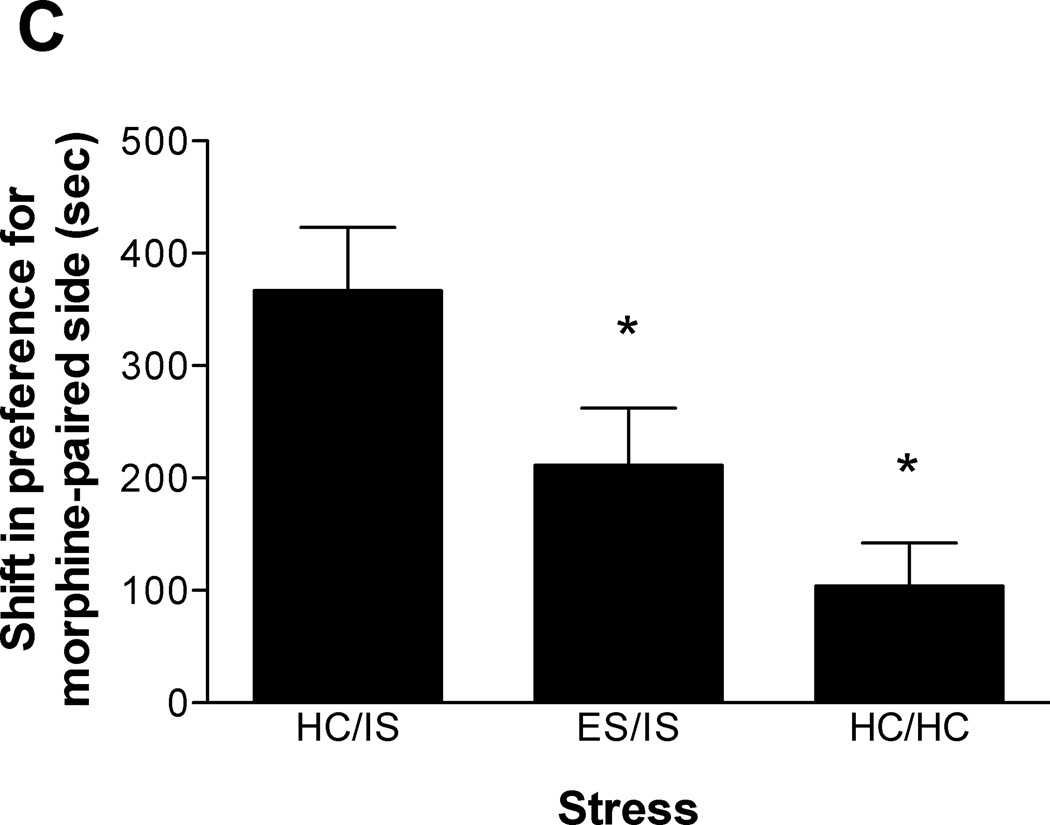
Figure 2.
A. Escapable tailshock (ES) 3 days prior to inescapable tailshock (IS) blocks potentiation of morphine conditioned place preference (CPP). Data are expressed as mean + SEM difference of time (sec) spent in the morphine-paired environment before and after conditioning. Positive scores indicate a shift in preference for the morphine-paired environment. *A single session of IS (HC/IS) potentiated morphine CPP as compared to behavioral immunization (ES/IS) and non-stressed controls (HC/HC) (p < 0.05). B. ES 14 days prior to IS blocks potentiation of morphine CPP. *A single session of IS (HC/IS) potentiated morphine CPP as compared to behavioral immunization (ES/IS) and non-stressed controls (HC/HC) (p < 0.05). C. ES 56 days prior to IS blocks potentiation of morphine CPP. *A single session of IS (HC/IS) potentiated morphine CPP as compared to behavioral immunization (ES/IS) and non-stressed controls (HC/HC) (p < 0.05).