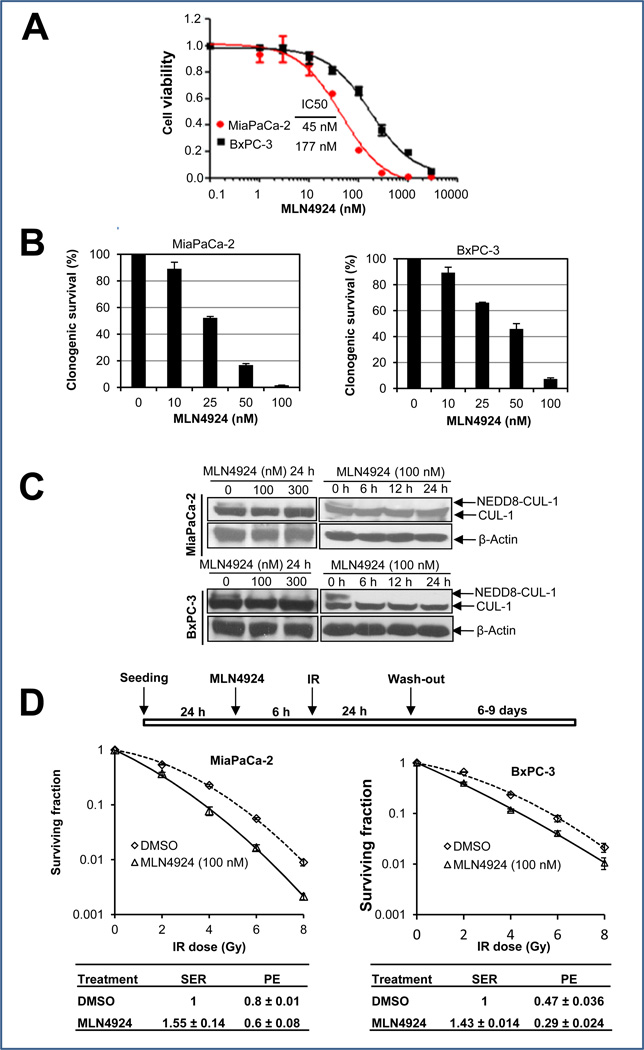
Figure 1. MLN4924 sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to radiation.
(A&B) Growth suppression of pancreatic cancer cells by MLN4924: Cells were seeded in 96-well plates in triplicates (A) or 60-mm dishes in duplicates (B), and treated with various concentrations of MLN4924 for 7 or 9 days, respectively. Cells were then lysed for ATPlite assay (A, mean ± SEM, n = 3) or the colonies with more than 50 cells were counted, following staining (B, mean ± SD, n = 2). (C) Inhibition of cullin-1 neddylation by MLN4924. Subconfluent cells were treated with MLN4924 at indicated concentrations or for indicated time periods, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with β-actin as a loading control. (D) Radiosensitization by MLN4924: Cells were seeded in 60-mm dishes in duplicate and treated with MLN4924 and radiation as indicated. The colonies with more than 50 cells were counted after 6–9 days. Surviving fraction was calculated as the proportion of seeded cells following irradiation to form colonies relative to that of untreated cells (mean ± SEM, n = 3). SER was calculated as the ratio of the mean inactivation dose under untreated control conditions divided by the mean inactivation dose after MLN4924 treatment. PE (plating efficiency was expressed as the percentage of the colonies formed out of cells seeded).