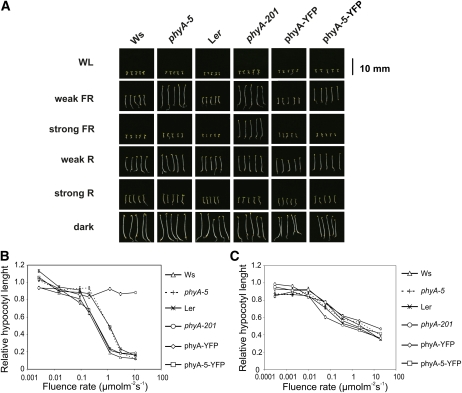
Figure 2.
The effect of phyA-5 mutation on the light-dependent phenotype of 4-d-old seedlings. A, Images of seedlings grown under constant irradiation for 4 d. WL, 100 μmol m−2 s−1 fluorescent white light; weak FR, 1 μmol m−2 s−1 FR light; strong FR, 10 μmol m−2 s−1 FR light; weak R, 0.002 μmol m−2 s−1 R light; strong R, 20 μmol m−2 s−1 R light; dark, etiolated seedlings. B, Fluence rate-dependent inhibition of hypocotyl elongation, measured on 4-d-old seedlings grown in FR light. The obtained values were normalized to the hypocotyl length of the corresponding dark-grown seedlings. Error bars indicate se. C, Fluence rate-dependent inhibition of hypocotyl elongation, measured on 4-d-old seedlings grown in R light. The obtained values were normalized to the hypocotyl length of the corresponding dark-grown seedlings. Error bars indicate se. Analyzed genotypes are as follows: Ws; phyA-5 mutant (ecotype Ws); Ler; phyA-201 (ecotype Ler); phyA-YFP, PHYA:PHYA-YFP in the phyA-201 background; phyA-5-YFP, PHYA:PHYA-5-YFP in the phyA-201 background. [See online article for color version of this figure.]