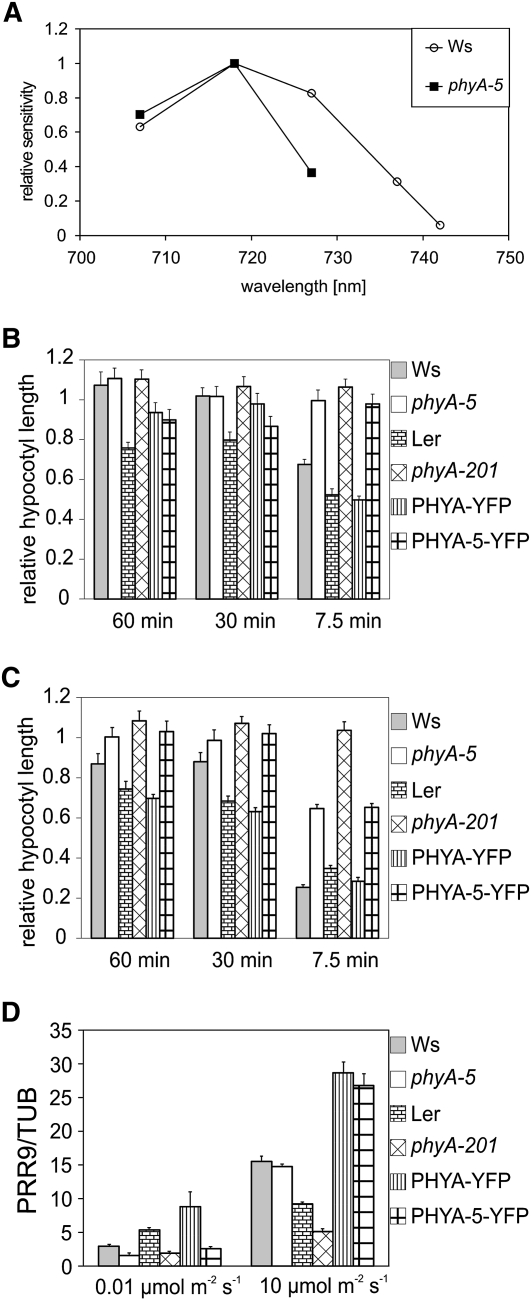
Figure 3.
The phyA-5 mutation affects spectral sensitivity and the VLFR. A, Action spectra for hypocotyl elongation in wild-type (Ws) and phyA-5 seedlings. The reciprocal value of the fluence rate that results in 60% inhibition of hypocotyl elongation compared with the corresponding dark controls was determined from the analysis of fluence rate response curves determined at different wavelengths. For better comparison, the highest value obtained in each line was set to 1, and all corresponding data were normalized to this value. B, Seedlings grown for 4 d in the dark were irradiated with 150-s FR (DAL715 filter) pulses of 0.6 μmol m−2 s−1 once every 60, 30, or 7.5 min. The hypocotyl lengths were measured after 4 d of growth, and each value obtained was normalized to the corresponding etiolated control. Error bars indicate se. C, The treatment and the analyzed lines were exactly as presented in B, with the exception of the intensity of the applied FR light pulse, which was 6 μmol m−2 s−1. Error bars indicate se. D, Four-day-old etiolated seedlings were irradiated with 0.01 or 10 μmol m−2 s−1 R light pulse for 1 min and were subsequently incubated for 60 min in the dark before sample collection. PRR9 mRNA level was determined by qRT-PCR. Data normalized to TUBULIN2/3 levels are shown. Error bars indicate se. Analyzed genotypes are as in Figure 2.