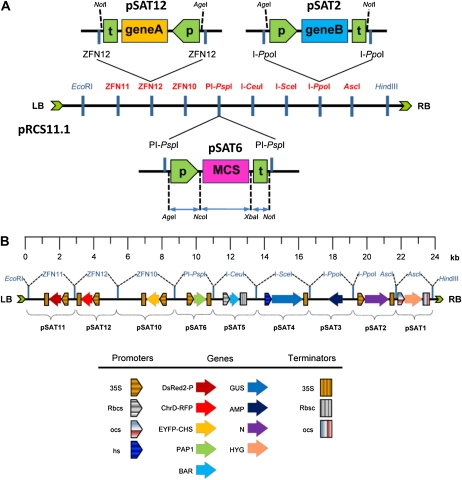
Figure 1.
General features of the ZFN- and homing endonuclease-mediated multigene binary vector assembly system. A, The general structure of a typical pSAT vector is exemplified by pSAT6, in which the promoter is flanked by the unique AgeI and NcoI sites, the terminator is flanked by the unique XbaI and NotI sites, the gene of interest is cloned into an extended MCS, and the entire plant expression cassette is flanked by recognition sites for ZFNs (e.g. ZFN12 in pSAT12) or homing endonuclease (e.g. PI-PspI in pSAT6). The ZFN and homing endonuclease recognition sites are shown on the binary pRCS11.1. Using ZFNs and homing endonucleases, up to nine expression cassettes can be transferred from the pSAT vectors into the T-DNA region of pRCS11.1. LB, Left border; P, promoter sequence; RB, right border; T, terminator sequence. B, Structure and scale of the pRCS11.1[1.HYG][2.N][3.AMP][4.GUS][5.BAR][6.PAP1][10.EYFP-CHS][11.DsRed2-P][12.ChrD-RFP] nine-transgene-long plant transformation binary vector. The general structure and direction of each expression cassette is shown. Promoters and terminators are as follow: 35S, double CaMV 35S; Rbcs, Rubisco small subunit; ocs, octopine synthase; hs, hsp18.1 heat shock. Proteins are as follow: DsRed2-P, P protein of SYNV fused to DsRed2; ChrD-RFP, chromoplast-specific carotenoid-associated protein ChrD fused to RFP; EYFP-CHS, chalcone synthase fused to EYFP; PAP1, Arabidopsis transcription factor production of anthocyanin pigment 1; BAR, Basta resistance-encoding gene; AMP, ampicillin resistance; N, N protein of SYNV; HYG, hygromycin resistance.