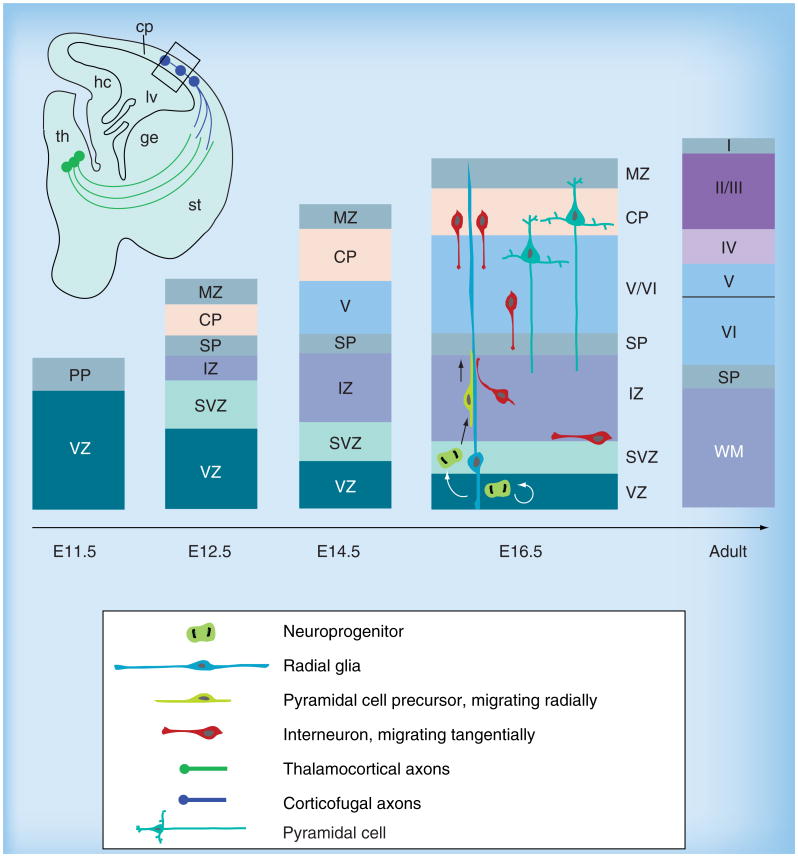
Figure 3. Generation of neuronal diversity in cortical formation.
The earliest born neurons form the PP, which is later split into the superfcial MZ and the deeper layer SP. Neuroprogenitors residing in the VZ and SVZ in mice produce pyramidal projection neurons in an ‘inside-out’ fashion, migrating radially towards the surface to populate the cp. The cp develops inbetween the MZ and SP and gives rise to the multilayered pattern, while the progenitor zones progressively reduce in size. The relationship between different populations of cells is depicted at E16.5. Radial glial cells divide symmetrically in the VZ to produce additional radial glial cells. A fraction of these depart from the VZ and migrate radially towards the pial surface, giving rise to different types of projection neurons. Interneurons migrate tangentially from the ganglionic eminence and enter the neocortex around E17. cp: Cortical plate; ge: Ganglionic eminence; hc: Hippocampus; lv: Lateral ventricle; MZ: Marginal zone; PP: Preplate; SP: subplate; st: Striatum; SVZ: Subventricular zone; th: Thalamus; VZ: Ventricular zone.