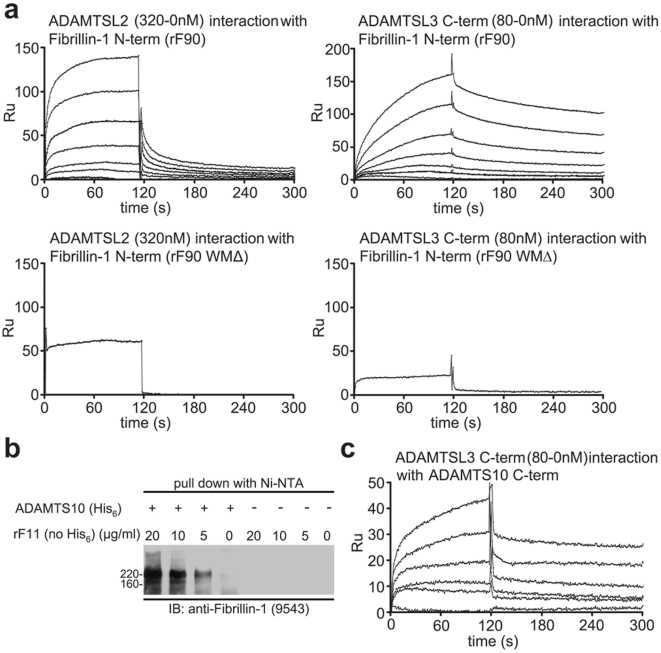
Figure 5. Biochemical analyses of interactions among ADAMTSL proteins, fibrillin-1, and ADAMTS-10.
(a) SPR sensorgrams showing binding of different concentrations of soluble ligands to the N-terminal half of fibrillin-1 (rF90), coupled onto a chip. Full-length ADAMTSL-2 (320-0 nM) interacts with rF90, as does the C-terminal end of ADAMTSL-3 (80-0 nM). No binding was detected when rF90WMΔ was used, demonstrating that the binding site for ADAMTSL proteins resides in the deleted region. (b) Fibrillin-1/ADAMTS-10 pull-down assay. Conditioned medium from transfected cells expressing full-length ADAMTS-10 with a C-terminal His6-tag was incubated with increasing amounts of rF11 (N-terminal half of fibrillin-1, similar to rF90 but lacking the His6-tag). ADAMTS-10 complexes were pulled down after incubation with Nickel NTA resin. SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-fibrillin-1 antibody (9543) showed the presence of fibrillin-1 in the pulled-down ADAMTS-10 complexes. Conditioned medium from untransfected cells (−) was subjected to the same procedure and served as a control. Even though rF11 was added in similar amounts to the control medium, no fibrillin-1 was pulled-down, demonstrating the specificity of the interaction between ADAMTS-10 and fibrillin-1. (c) SPR sensorgrams showing binding of different concentrations (80-0 nM) of soluble C-terminal ADAMTSL-3 to the C-terminal end of ADAMTS-10, coupled to a chip. Calculated KD for this interaction was 2 nM.