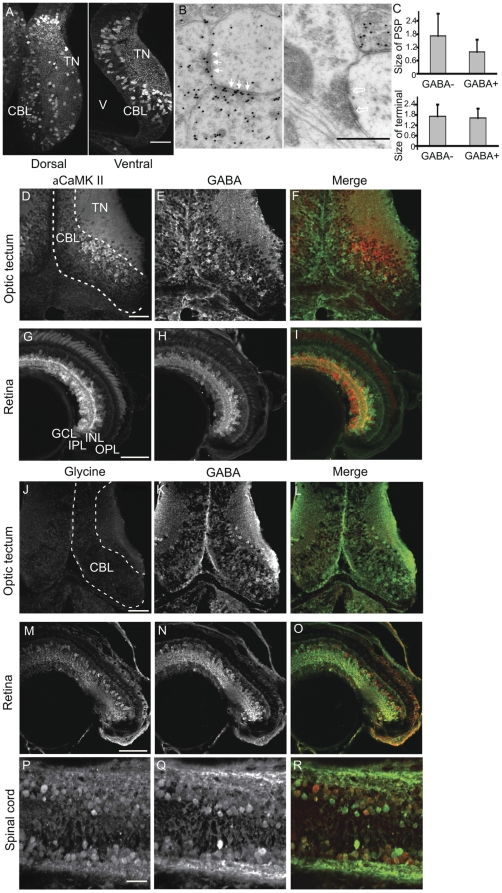
Figure 1. Immunocharacterization of stage 47 Xenopus laevis visual system.
A. GABA immunofluorescent labeling in 200 nm LR White-embedded horizontal sections of optic tectum. GABA-positive somata are scattered throughout the cell body layer (CBL) and constitute the majority of neurons in the tectal neuropil (TN). The proliferative cells lining the ventricle (V) and in caudal tectum are not GABA immunoreactive. B. Ultrastructure of GABAergic synapses identified by post-embedding immunogold labeling in 70 nm sections from epoxy-resin embedded tissue. Electron micrograph of the tectal neuropil, showing two GABAergic presynaptic profiles forming symmetric contacts with a non-GABAergic postsynaptic profile (solid arrows). On the right a postsynaptic profile receives an asymmetric, non-GABAergic synaptic input with a prominent postsynaptic density (hollow arrows). C. Size comparison for GABA-negative (N = 28) and GABA-positive (N = 12) post-synaptic profiles (PSPs) and presynaptic terminals. D–F. Cryosections through optic tectum immunostained for αCaMKII (D) and GABA (E), and the merge of a CaMKII (red) and GABA (green) immunolabeling (F). There is little overlap of the CaMKII- and GABA-immunolabeled cells. G–I. αCaMKII (G) and GABA (H) immunolabeling in the retina. Most RGCs are αCaMKII immunoreactive. Neurons in the INL are predominately GABA-immunoreactive. Double labeling the retina for αCaMKII (H) and GABA (I) immunopositive cells shows little overlap in the cell body layers. J–L. Immunostaining for glycine and GABA reveals no detectable glycine label in the tectum (J). M–O. In the retina glycine-positive amacrine cells (M) are prominent in the INL (red in O) and are distinct from the GABAergic amacrine cells (N), shown as green in O. A few GABA-positive displaced amacrine cell bodies are also found in the ganglion cell layer (H, I, N, O). P–R. Immunolabeling for glycine (P, red in R) and GABA (Q, green in R) in the spinal cord shows neurons in the spinal cord can be immunoreactive for both transmitters (R). Scale Bars in A: 150 µm, in B: 500 nm, in D, G, J, M, and P: 50 µm, and apply to all images in the corresponding row.