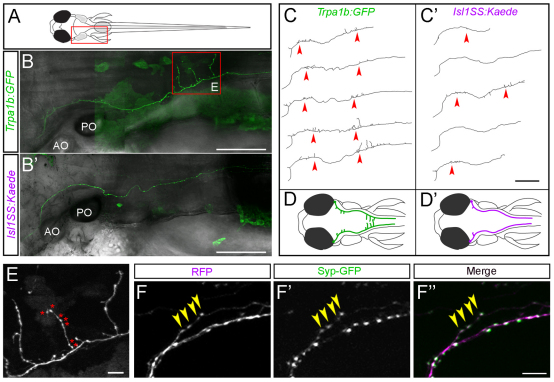
Fig. 2.
Mosaic single-cell labeling of trigeminal sensory neuron subtypes. (A) Schematic of a 5-dpf larval zebrafish, viewed from the dorsal side. The boxed area corresponds to the imaged areas shown in B,B′. (B,B′) In vivo imaging of single trigeminal sensory neurons. Fluorescent image is shown in green and bright-field image is superimposed in gray. Extensive branch growth is seen in the Trpa1b subset (B), but not the Isl1SS subset (B′). Boxed area corresponds to imaged area shown in E. (C,C′) Axon traces of multiple trigeminal sensory neurons are shown for both subtypes. Red arrowheads point to branches that form along the main axon tract. (D,D′) Illustrations of trigeminal afferents from Trpa1b (D) and Isl1SS (D′) subtypes. (E) High-magnification image of boxed area in B. Trpa1b axon extends branches and forms numerous varicosities (asterisks). (F-F″) Trigeminal axon labeled with cytoplasmic RFP (magenta, F) and Synaptophysin-GFP (Syp-GFP, green, F′), a fluorescent label for synaptic vesicles (with merge in F″). The presence of varicosities reliably predicts the presence of Syp-GFP puncta (yellow arrowheads). AO, anterior otolith; PO, posterior otolith. Scale bars: 100 μm in B-C′; 10 μm in E-F″.