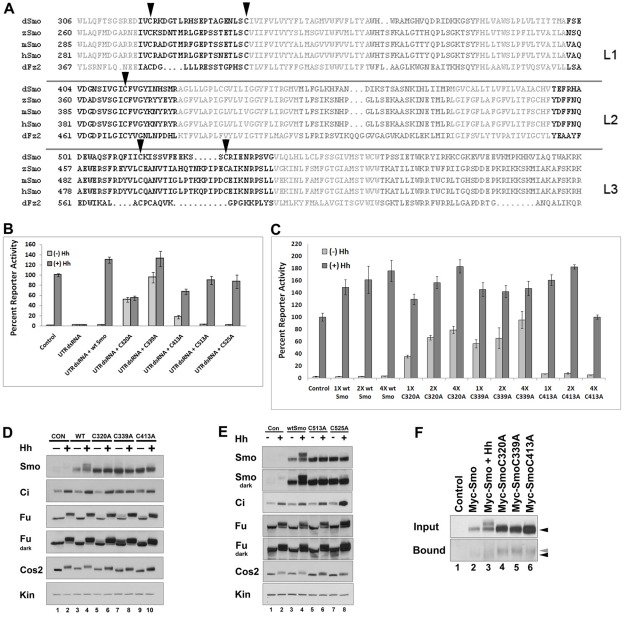
Fig. 1.
Conserved loop cysteines play a regulatory role in Smo signaling. (A) Alignment of Drosophila residues 306-596 against sequences of zebrafish, mouse, and human Smo proteins and Drosophila Frizzled2. Transmembrane residues are light gray, intracellular loops are dark gray and extracellular loops are black. Conserved loop 1 (L1) C320 and C339, loop 2 (L2) C413 and loop 3 (L3) C513 and C525 cysteines (Drosophila numbering) are indicated by arrowheads. Alignments were generated using StrapAlign (http://www.bioinformatics.org/strap/). (B) EC1 and EC2 cysteine mutants differentially rescue smo knockdown. Cl8 cells were treated with control or smo 5′UTR dsRNA and transfected with the indicated pAc-myc-smo expression vector. The ability of wild type or each of the Myc-Smo C to A mutants to rescue ptc-luciferase activity in presence of control vector (light gray bars) or pAc-hh (dark gray bars) is shown. The Hh-induced level of activity obtained in the presence of control dsRNA was set to 100%, and percent reporter activity relative to this value is shown. Activity levels are normalized to a pAc-renilla transfection control. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). (C) Loop 1 C to A mutants are dominant positive. Myc-Smo C to A mutant proteins were expressed in Cl8 cells with or without Hh, as indicated. Reporter activity was assessed as in B. In each case, 1X corresponds to 50 ng pAc-myc-smo. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (D) EC1 and EC2 cysteine mutants differentially activate downstream effectors. Lysates of Cl8 cells expressing wild-type or C to A mutant Smo proteins in the presence of pAc-hh (+) or empty vector (–) were examined by western blot. Short (Fu) and long (Fu dark) exposures are shown to visualize phosphorylation-induced mobility shifts (lanes 5 and 7). Samples are normalized to protein. Kinesin (Kin) serves as a loading control. (E) EC3 C to A mutants do not induce ligand-independent activation of downstream effectors. Lysates of Cl8 cells transfected with wild-type or C to A mutant pAc-myc-smo expression vectors with pAc-hh (+) or empty vector (–) were examined by western blot. Samples are normalized to protein. Kin serves as a loading control. (F) C to A mutants have free cysteines. Membrane fractions prepared from cells transfected with the indicated smo constructs were treated with maleimide-PEG11-biotin to label free cysteines. Biotinylated proteins were precipitated on NeutrAvidin agarose and surveyed by western blot against Smo (bottom panel). Wild-type and mutant Smo proteins demonstrate similar mobility before treatment (upper panel, black arrow). C to A mutants in affinity complexes migrate more slowly than wild-type Smo (bottom panel, gray arrow compared with black).