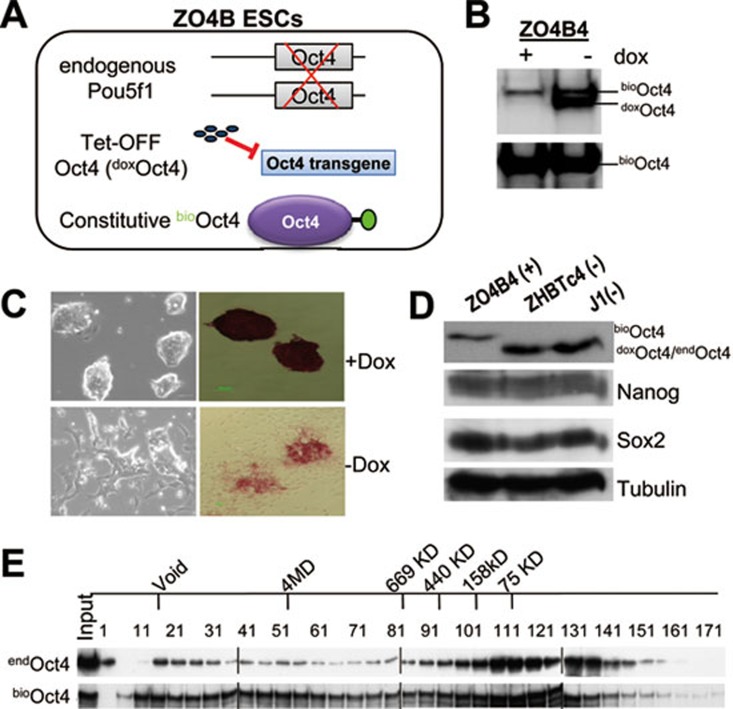
Figure 1.
Establishment of in vivo biotinylation system for affinity purification of Oct4 protein complexes in modified ZHBTc4 (ZO4B) ESCs. (A) Schematic depiction of the modified ZHBTc4 ESCs expressing biotinylated Oct4 protein. (B) Western blot analysis of relative expression levels of dox suppressible (doxOct4) and constitutively active biotinylated Oct4 (bioOct4) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of dox treatment. Top, anti-Oct4 blot; Bottom, SA-HRP blot. (C) Morphology of ZO4B4 ESCs in the presence (top) or absence (bottom) of dox. Images of colonies that are unstained (left panels) or stained for AP activity (right panels) are shown. (D) Normal expression levels of Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in ZO4B4, ZHBTc4, and J1 ESCs in the presence (+) or absence (−) of dox treatment. (E) Size exclusion chromatography (gel filtration) of nuclear extracts of J1 (top) and ZO4B4 (bottom) ESCs. Endogenous Oct4 protein complexes (endOct4) in wild-type J1 ESCs were detected by anti-Oct4 western blot (top), and the Oct4 protein complexes in ZO4B4 ESCs (bioOct4) were also detected by anti-Oct4 western blot (bottom).