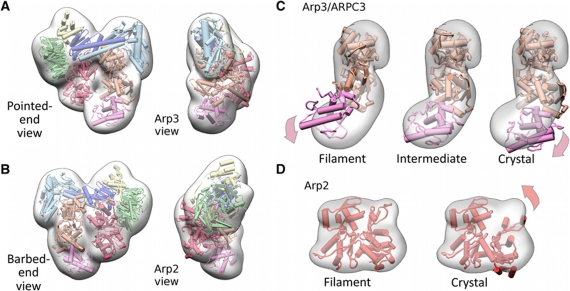
Figure 2.
Molecular model of the NPF-bound conformation of Arp2/3 complex. (A, B) Four orthogonal views of the molecular model of the NPF-bound conformation of Arp2/3 complex in cartoon representation and a transparent surface representation of the class II reconstruction from which the NPF density was removed are shown (see Materials and methods model building section for details). The colour scheme of the Arp2/3 subunits follows that in Figure 1D. The excellent visual fit indicates that the conformational changes induced by NPF binding are well accounted for our modelling at the resolution of the reconstruction. (C) Fits of Arp3/ARPC3 (orange, magenta, respectively) models with various states of the Arp3 nucleotide-binding cleft into the transparent surface representation of the density module for these subunits. The view corresponds to the pointed end view in Figure 2A. The models were aligned to subdomain 1 of Arp3 and the contour level of the density presentation was chosen to be slightly lower than that displayed in (A, B) for illustration purposes. Filament and crystal (1K8K) conformations denote closed and open nucleotide-binding cleft, respectively. The fits indicate that Arp3 adopts an intermediate cleft conformation. (D) Fit of two Arp2 models into the Arp2 density module. Subdomains 1 and 2 of Arp2 crystal model were completed using the structure of an actin monomer (1J6Z) overlaid with subdomains 3 and 4 of Arp2. The fits indicate that Arp2 adopts a conformation similar to a subunit in an actin filament.