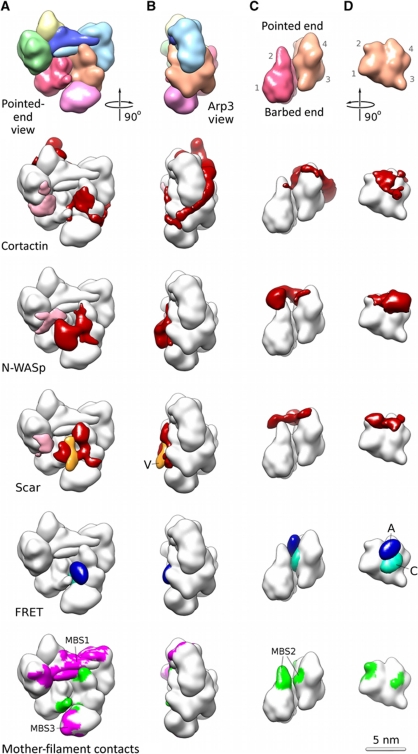
Figure 3.
Localization of the NPF on the Arp2/3 complex. (A) The pointed end view of the entire Arp2/3 complex, (B) the Arp3 view of the entire complex, (C) the side view of the Arp2/Arp3 heterodimer in the NPF-bound conformation and (D) the Arp3 subunit with Arp2 removed for clarity. The Arp subdomains are marked in the first row of (C, D). The first row shows a low-resolution representation of the NPF-bound Arp2/3 conformation (model of class II, Figure 2A and B) in the colour scheme defined in Figure 1D. The row labelled cortactin shows the density attributable to the bound cortactin (red) mapped onto the low-resolution representation shown in the first row (white). The extra density at ARPC1 (in pink) can largely be attributed for by the ∼50 residues missing in the crystal structure from ARPC1 (∼30 residues) and the C-terminus of ARPC2 (∼20 residues). The row labelled ‘N-WASp’ shows the density attributable to the bound N-WASp/Nck (red). Most of the N-WASp/Nck is not visible in our maps and appears to be disordered as suggested by the large variance peak in this region (peak 3 in Figure 1F). The row labelled ‘Scar’ shows the density attributable for by Scar-VCA (red) and the additional density present in the Scar-VCA construct with an N-terminal MBP tag (orange). This location marks the N-terminus of the V region (V). The density does not account for all of MBP, indicating that it is flexibly attached. The row labelled ‘FRET’ shows the location of the C-terminus of the A region (blue, marked A) and the N-terminus of the C region (cyan, marked C). The peaks are contoured to contain 0.5 of the entire probability density. The location determined by FRET is fully consistent with the NPF densities obtained by electron microscopy. The MBS row shows the mother-filament contacts determined previously by electron tomography of fully assembled Arp2/3-mediated branch junctions (Rouiller et al, 2008). It is clear that the NPF locations determined here overlap with the mother-filament contacts at the MBS2-binding site (green) while the MBS1 and MBS3-binding sites (magenta) remain accessible.