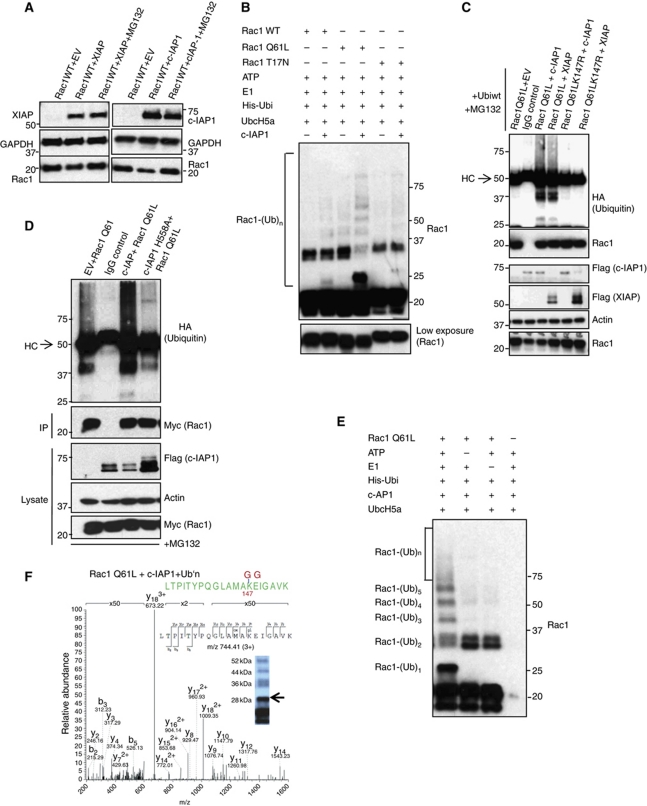
Figure 5.
Binding of IAPs to Rac1 promotes Rac1 polyubiquitination and degradation. (A) The rescue in the levels of Rac1 under the influence of proteasomal inhibitors MG132 upon IAP overexpression is monitored by western blotting. (B) c-IAP1 directly ubiquitinates Rac1. Purified recombinant Rac1 proteins with various mutations were subjected to in-vitro ubiquitination with c-IAP1 as described in Materials and methods. The conjugation of ubiquitin to Rac1 was monitored by immunoblots. The lower exposure of Rac1 was shown below. (C) XIAP and c-IAP1 promoted the polyubiquitination of activated Rac1. 293T cells were transfected with Myc–Rac1Q61L or Myc–Rac1Q61LK147R in combination with Flag–IAPs and HA–ubiquitin constructs. Rac1Q61L was immunoprecipitated by using Myc antibody and the immunocomplexes were western blotted for HA (ubiquitin), Rac1 and Flag for IAPs. The cells were treated with MG132 for 6 h before lysing. (D) Ubiquitination of Myc–Rac1Q61L by c-IAP1 and c-IAPH588A in 293T cells is analysed as mentioned in (C). (E) c-IAP1 directly ubiquitinates Rac1 at lysine 147. Recombinant Rac1Q61L was subjected to an in-vitro ubiquitination reaction as mentioned in Materials and methods with c-IAP1. The modification of Rac1 protein was monitored by immunoblots. (F) Samples from in-vitro ubiquitination reaction of Rac1 with c-IAP1 (E) were subjected to mass spectrometric analysis after digestion with trypsin. MS/MS spectrum of the Rac1 peptide carrying Gly-Gly modification at position K147 is shown. The mass of the triply charged precursor ion at 744.41 was measured with a mass deviation of 0.08 p.p.m. Arrow indicates the gel band where the peptide was detected. Figure source data can be found in Supplementary data.