Figure 1.
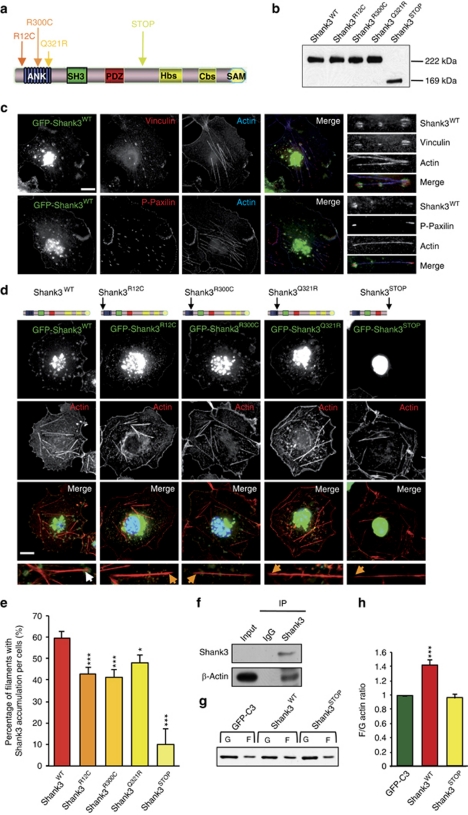
Mutations in Shank3 affect its recruitment to the tips of actin filaments and actin polymerization. (a) Localization of rare non-synonymous variations or truncating SHANK3 mutations identified in autism spectrum disorder.6, 7 ANK, ankyrin repeats; Cbs, cortactin-binding site; Hbs, Homer-binding site; PDZ, postsynaptic density 95/discs large/zona occludens-1 homology domain; SAM, sterile alpha motif domain; SH3, Src homology 3 domain. (b) Western blot analysis of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) constructs expressed in HEK293T cells. We observed similar sizes of Shank3WT and fusion proteins carrying point mutations (Shank3R12C, Shank3R300C and Shank3Q321R). The frameshift mutation results in a truncated protein (222 kDa GFP–Shank3WT and 169 kDa GFP–Shank3STOP). (c) Localization of Shank3WT in COS-7 cells transiently transfected with GFP–Shank3WT (green) and labeled with phalloidin 647 to visualize F-actin (blue) and with anti-vinculin or anti-phospho-paxillin (red), two focal adhesion proteins. Shank3WT is located at the membrane and in intracellular clusters that colocalize with vinculin or phospho-paxillin at the tips of actin filaments. On the right side, magnification of representative stress fibers with clusters of Shank3WT. (d) Localization of Shank3WT and mutated forms in COS-7 cells. COS-7 cells transiently transfected with GFP–Shank3WT or mutated forms (green), and labeled with phalloidin 546 to visualize F-actin (red) and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole to visualize the nucleus (blue). Shank3R12C, Shank3R300C and Shank3Q321R are located at the membrane and in intracellular clusters. Conversely, Shank3STOP is restricted to around the nucleus. (e) Quantification of the accumulation of GFP constructs at the tips of actin filaments. Percentage of filaments with Shank3 clusters per cell (%). This accumulation is significantly reduced with mutated Shank3 and absent with Shank3STOP (n=30–40 cells). Scale bars represent 15 μm. (f) Coimmunoprecipitation of Shank3 and actin in an adult rat brain. Lysate (input) was incubated with control immunoglobulin or anti-Shank3. Immunoprecipitation was performed, followed by western blotting using anti-β-actin. (g) Shank3STOP inhibits the effect of Shank3WT on actin polymerization. HEK293T were transiently co-transfected with red fluorescent protein–actin and GFP–C3 (control), GFP–Shank3WT or GFP–Shank3STOP. Representative immunoblots of G-actin (G) and F-actin (F) fractions obtained with an Actin Polymerization Assay kit. G-actin and F-actin were probed with anti-actin antibody. (h) Ratio of F-actin/G-actin was measured for each condition. The ratio is normalized to GFP–C3 and is represented as the mean±s.e.m. Shank3WT enhances the polymerization of actin (***P<0.001; n=6 independent experiments). Shank3STOP inhibits the effect of Shank3 on actin polymerization.