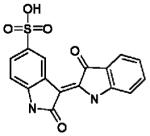
Table 1. Confirmed lead structures inhibiting EtCRK2.
| Structure | Name | Structure class | IC50 [μM] | Ki [μM] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HsCDK2 | EtCRK2 | HsCDK2 | EtCRK2 | |||
|
Indirubin-5-sulfonate | Oxindole | 0.23±0.11 | 0.67±0.19 | 0.08±0.01 | 0.17±0.03 |

|
BES062021 | Rhodanine-oxindole | 26±19 | 23±14 | 17±8 | 16±9 |

|
BES143551 | Naphtolactame | 12±7 | 36±8 | 2±1 | 6±2 |

|
BES241415 | Benzimidazole-carbonitrile | 41±13 | 61±27 | 41±13 | 83±29 |

|
BES252034 | Benzimidazole | 35±3 | 15±3 | 8±2 | 8±2 |
In silico hits were verified against EtCRK2 and HsCDK2. Due to the high sequence similarity between HsCDK2 and GgCDK3, HsCDK2 served as model for GgCDK3, which was not available. Indirubin-5-sulfonate[33] was used as standard HsCDK2 inhibitor. Four confirmed leads have been identified belonging to the structural class rhodanine-oxindoles, naphtolactames, benzimidazole-carbonitriles and benzimidazoles. Results are expressed as mean IC50 and mean Ki values ± SD in three to four different experiments (n=3-4).
