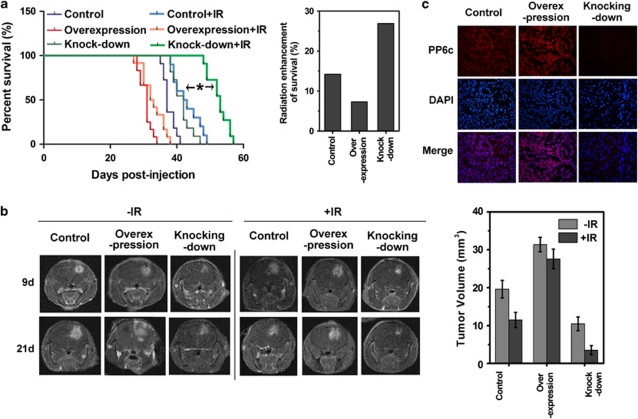
Figure 5.
Small interfering (siRNA) knockdown of PP6 catalytic subunit (PP6c) improves the radiation therapeutic efficacy on the mice bearing orthotopic xenografted glioblastoma. (a) The mice were euthanized at the time of reaching a moribund condition, and all survival times in each group were analyzed using Kaplan–Meier method. This experiment was independently repeated two times, six mice in each group at the start time point. The analyzed mice with radiation treatment in empty virus group (control), PP6c knocking-down or PP6c overexpression group were 10, 11, 12, respectively, while the mice without radiation treatment in the control group, PP6c knocking-down or PP6c overexpression group were 11, 11, 12, respectively. The radiation enhancements of survival time in each group were calculated by the formula: the survival time with radiation divided by the survival time without radiation. The significance of radiation enhancement difference between control siRNA group and PP6c siRNA group were analyzed by the χ2 method (*P<0.001). (b) The representative tumor pictures from the PP6c overexpression, the PP6c knocking-down or the control group were captured by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) imaging at the 9th and 21st day with (+IR (ionizing radiation)) or without radiation treatment (−IR), and the tumor volumes were calculated by the formula: ½ × L × S2 (L: maximum length; S: minimum length). (c) The representative PP6c immunofluorescence staining (red) in glioblastoma sections from the PP6c overexpression, the PP6c knocking-down or the control group