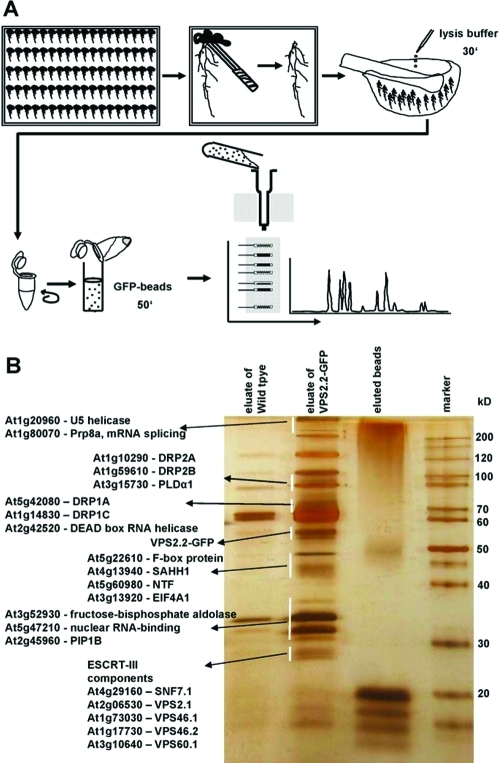
Figure 2.
Strategy to purify and identify AtVPS2.2-GFP interacting proteins. (A) Roots were separated from seedlings, cushed in liquid nitrogen, lysed with cracking buffer on ice and centrifuged to separate cell debris. Anti-GFP μMACS MicroBeads were added to the supernatant, mixed by rotating and after incubation on ice applied onto μ Columns. The eluted proteins were separated on a denaturing 12% (w/v) PAGE and visualized with a LC–MS/MS compatible silver staining protocol. Lanes were excised into up to 29 fractions and subjected to nanoelectrospray LC–MS/MS sequencing. (B) Example of a silver stained PAGE showing the eluates from extracts of control roots (wildtype), transgenes expressing AtVPS2.2-GFP and the eluted beads. Indicated are proteins which have been specifically enriched by this method.