Figure 1.
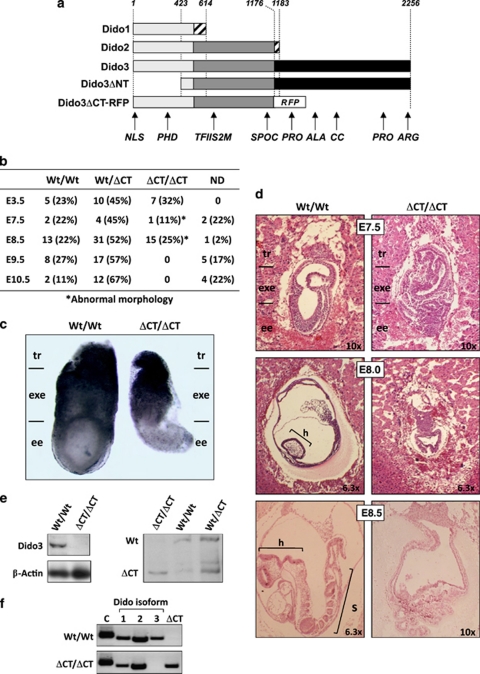
Ablation of Dido3 is embryonic lethal. (a) The three isoforms encoded by the Dido locus (Dido1, Dido2 and Dido3), as well as the two Dido loss-of-function mutants studied so far (DidoΔNT, previously published;2 Dido3ΔCT-RFP, this study). Common and isoform-specific portions of the Dido proteins are indicated (light gray, regions common to all three Dido isoforms; dark gray, regions common to Dido2 and Dido3; black, Dido3-specific regions; hatching, short isoform-specific C-terminal fragments). The location of the in-frame RFP cassette in the Dido3ΔCT-RFP mutant is indicated (RFP). Numbers denote amino acid position, counted from the N-terminus of the three Dido isoforms. Abbreviations below indicate the approximate positions of Dido functional domains (NLS, nuclear localization signal; PHD, plant homeodomain; TFIIS2M, transcription factor S domain II module; SPOC, Spen paralog and ortholog C-terminal domain; PRO, proline-rich domain; ALA, alanine-rich domain; CC, coiled-coil domain; ARG, arginine-rich domain). (b) Ablation of Dido3 is embryonic lethal. Embryos from intercrosses of Dido3ΔCT-RFP heterozygous mice were genotyped by PCR at different gestational stages. Embryonic days (E) are days post-coitum. Wt/Wt, Wt for Dido3; Wt/ΔCT, heterozygous for Dido3ΔCT-RFP; ΔCT/ΔCT, homozygous for Dido3ΔCT-RFP; ND, not determined due to embryo resorption. An asterisk indicates the presence of overt morphological alterations. (c) Comparison of whole Wt/Wt and ΔCT/ΔCT embryos at E7.5. Regions corresponding to the trophoblast (tr), extraembryonic ectoderm (exe) and embryonic ectoderm (ee) are indicated. (d) Histological comparison of whole Wt/Wt and ΔCT/ΔCT embryos. HE-stained sections of Wt/Wt and ΔCT/ΔCT embryos at E7.5, E8.0 and E8.5 are shown at indicated magnifications. Embryonic regions correspond to tr, exe and ee, as well as head (h) and somites (s). (e) Lysates of Wt/Wt and ΔCT/ΔCT embryos at E7.5 were analyzed by western blot with an anti-Dido3 C-terminus-specific antibody. β-actin was used as loading control (left). The anti-common amino-terminal segment antibody to the N-terminal portion of Dido, common to all Dido isoforms,3 was used to assay lysates of Wt/Wt, Wt/ΔCT and ΔCT/ΔCT embryos at E7.5 for expression of Dido3 and Dido3ΔCT-RFP (right). (f) RT-PCR was used to monitor Wt/Wt and ΔCT/ΔCT E7.5 embryos for expression of the splice variants Dido1, Dido2, Dido3 (1, 2 and 3) and Dido3ΔCT-RFP (ΔCT) using β-actin as control (C)