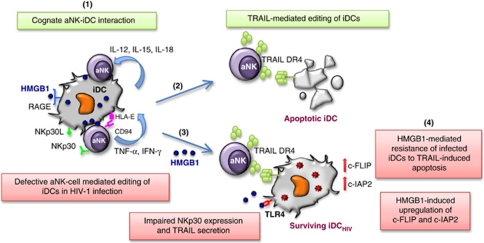
Figure 5.
Impact of HIV-1 infection on NK cell-mediated editing of iDCs. NK cells are involved in the positive selection of DCs through the editing process, which is required to keep in check the quality of DCs prone to mature and further present the antigens to T cells. Thus, cognate interaction between aNK and iDC may lead to the killing of iDC (1). NK cell-dependent killing of iDCs involves the activating NKp30 receptor (1) and the DR4/TRAIL death receptor pathway (2). HIV-1 infection induces a defective editing process. NK cells show a decreased ability to kill infected DCs associated with impaired NKp30 expression and TRAIL secretion (3), and infected DCs become resistant to NK-mediated killing due to the upregulation of two anti-apoptotic molecules, c-FLIP and c-IAP2 (4). HMGB1 induces these two potent inhibitors of apoptosis in infected DCs, thus making them resistant to NK killing