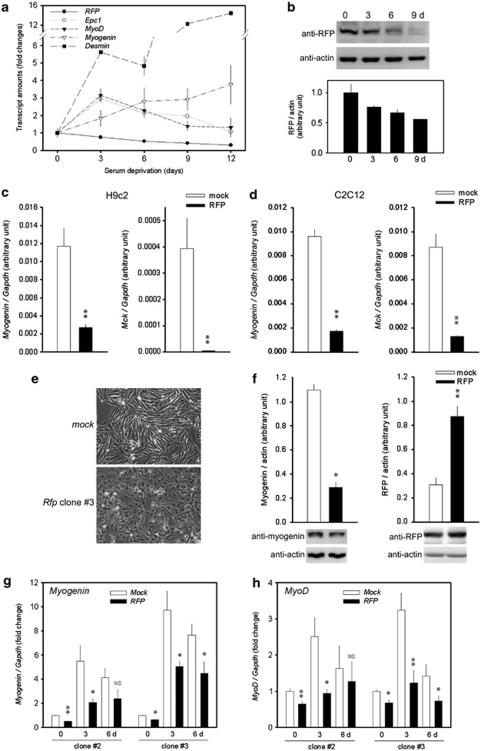
Figure 2.
RFP inhibits skeletal muscle differentiation. (a) Transcripts for Rfp, Epc1, MyoD, myogenin, and desmin were detected by qRT-PCR. C2C12 cells were forced to undergo differentiation into skeletal myocytes by replacing growth medium with differentiation medium. The expression of Rfp was gradually reduced during myoblast differentiation, whereas that of Epc1 was increased. Muscle-specific genes such as myogenin, MyoD, and desmin were upregulated by serum deprivation. The results from 4∼6 samples were shown. (b) The changes in Rfp protein amounts were also shown in primary cultured myoblasts cells isolated from the hamstring muscles of mice. Lower panel: quantification results from three independent sets of western blots. (c) Decreased myogenin and Mck transcript levels in RFP-overexpressing H9c2 cell lines. Transcript levels of myogenin and Mck were measured by qRT-PCR. (d) Transcripts for myogenin and Mck were measured by qRT-PCR in RFP-overexpressing C2C12 cells. (e) Impaired myotube formation of RFP-expressing cells. Mock- or RFP- expressing H9c2 cells were grown in differentiation media for 6 days. Mock-cells were elongated by serum deprivation, whereas RFP-cells were not. (f) Serum deprivation failed to induce myogenin in RFP-expressing cell lines. Band intensities from three independent sets of western blot analysis were averaged. (g and h) Transcript levels of myogenin (g) and MyoD (h) in two clones of RFP-overexpressing H9c2 cells were measured by qRT-PCR. NS, not significant. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with mock-transfected cells