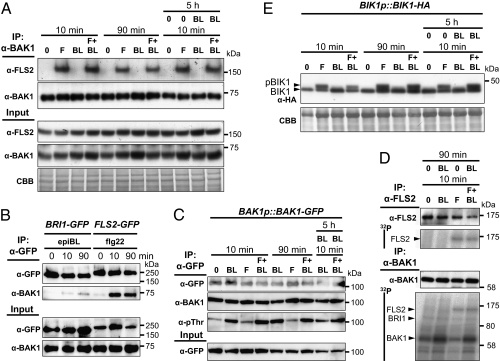
Fig. 4.
EpiBL perception does not affect the dynamic and the activity of the FLS2–BAK1–BIK1 complex. (A) IP of BAK1 in Col-0 seedlings treated with 1 μM flg22 (F) and/or epiBL (BL) for 10 min or 90 min (with or without 5 h epiBL pretreatment). Coimmunoprecipitated proteins were further analyzed by using anti-FLS2 or anti-BAK1 antibodies. (B) IP of GFP-tagged proteins from BRI1-eGFP or FLS2-3myc-GFP seedlings treated with 1 μM epiBL or flg22 (respectively) for 0, 10, and 90 min. Coimmunoprecipitated proteins were further analyzed by using anti-GFP or anti-BAK1 antibodies. (C) IP of BAK1-GFP proteins from transgenic seedlings treated as in A. Immunoblot is analyzed by using anti-BAK1 and anti-pThr antibodies. (D) IP of FLS2 or BAK1 from Col-0 seedlings treated with 1 μM flg22 (F) and/or epiBL (BL) for 10 min (with or without 90 min epiBL pretreatment). Immunoprecipitated proteins were then incubated in presence of radioactive [32P]γ-ATP. Immunoblots are analyzed by using anti-FLS2 or anti-BAK1 antibodies. In vitro phosphorylation is revealed in the autoradiogram (i.e., 32P). (E) BIK1 phosphorylation (detected as a band shift) in BIK1-HA seedlings treated as in A. The blots stained with CBB are presented to show equal loading. Molecular weights (in kDa) are indicated. Similar results were observed in at least two independent experiments.