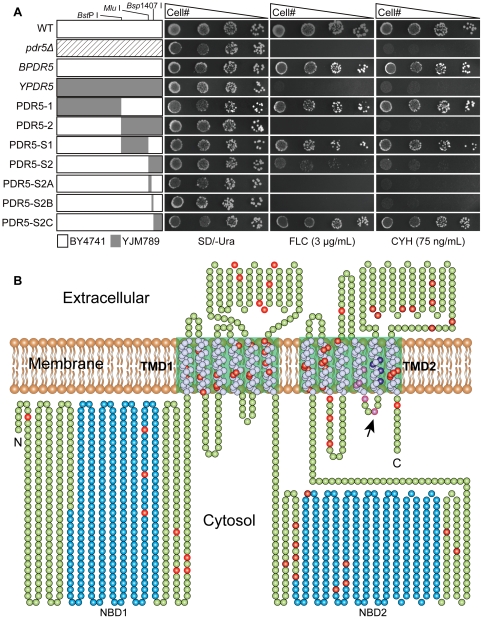
Figure 1. Identification of residues important for Pdr5p function and distribution of mutations in YJM789 Pdr5p.
(A) Segmental replacement of BY4741 PDR5 and drug resistance profiles of pdr5Δ S. cerevisiae cells expressing wild type and chimeric PDR5s by spot assay. Various regions of BY4741 PDR5 are segmentally replaced by corresponding segments from YPDR5. Segments from BY4741 and YJM789 PDR5 are shown as white and grey rectangles, respectively. The unique Bsp I, Mlu I, Bsp1407 I restriction sites, which were used to construct PDR5 chimeras are marked. Five-fold serial dilutions of pdr5Δ mutant carrying different PDR5 constructs were spotted on SD/-Ura media in the absence and the presence of 3 µg/mL fluconazole or 75 ng/mL cycloheximide. Plates were incubated for 72 hours at 30°C. (B) The topological model is based on the molecular modeling study of Pdr5p [11]. Two-dimensional schematic cartoon of Pdr5p shows the 12 predicted membrane spanning helices (white spheres) and two NBDs (blue spheres). The green boxed areas indicate the TMDs. Divergent residues between BY4741 and YJM789 are shown as red, purple and dark blue spheres, respectively. Ala 1352 is indicated by black arrow.