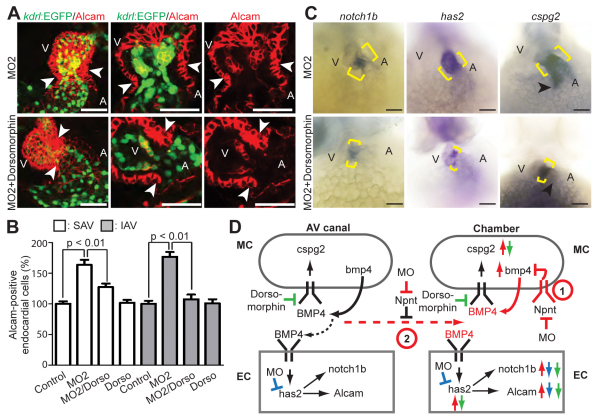
Fig. 7.
Inhibition of BMP signaling reduces AV canal expansion. (A) Projections of confocal images and confocal sections of hearts of MO2-injected Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 zebrafish embryos at 52 hpf with and without dorsomorphin treatment stained for Alcam (red, indicating myocardium and differentiated endocardial cells). (B) Quantitative analysis. Inhibition of BMP signaling by dorsomorphin (Dorso) in the npnt morphants rescued the AV canal endocardium extension (mean ± s.e.m.). SAV, superior AV; IAV, inferior AV. (C) Bright-field images of 52 hpf untreated and dorsomorphin-treated npnt morphants after whole-mount in situ hybridization for notch1b, cspg2 and has2 expression. Dorsomorphin treatment reduced the expression of notch1b and has2 at the AV boundary in npnt morphants (brackets). Moreover, ectopic expression of cspg2 at the inflow tract in npnt morphants is abolished (arrowheads) and cspg2 expression at the AV boundary is partially rescued. (D) Model of the regulatory role of Npnt. 1 and 2 are two possible mechanisms of how Npnt affects Bmp4 signaling. (1) Npnt activates a receptor that is expressed in the chamber myocardium to repress Bmp4 signaling. (2) Npnt inhibits diffusion of Bmp4, resulting in autocrine signaling. Arrows indicate changes after Npnt depletion in wild type (red) or upon has2 depletion (blue) or dorsomorphin treatment (green) in npnt morphants. Red dashed arrow indicates Bmp4 diffusion in the npnt morphant. Black dashed arrow indicates controlled Bmp4 diffusion in the wild type. A, atrium; V, ventricle; EC, endocardium; MC, myocardium; MO, morpholino. Scale bars: 50 μm.