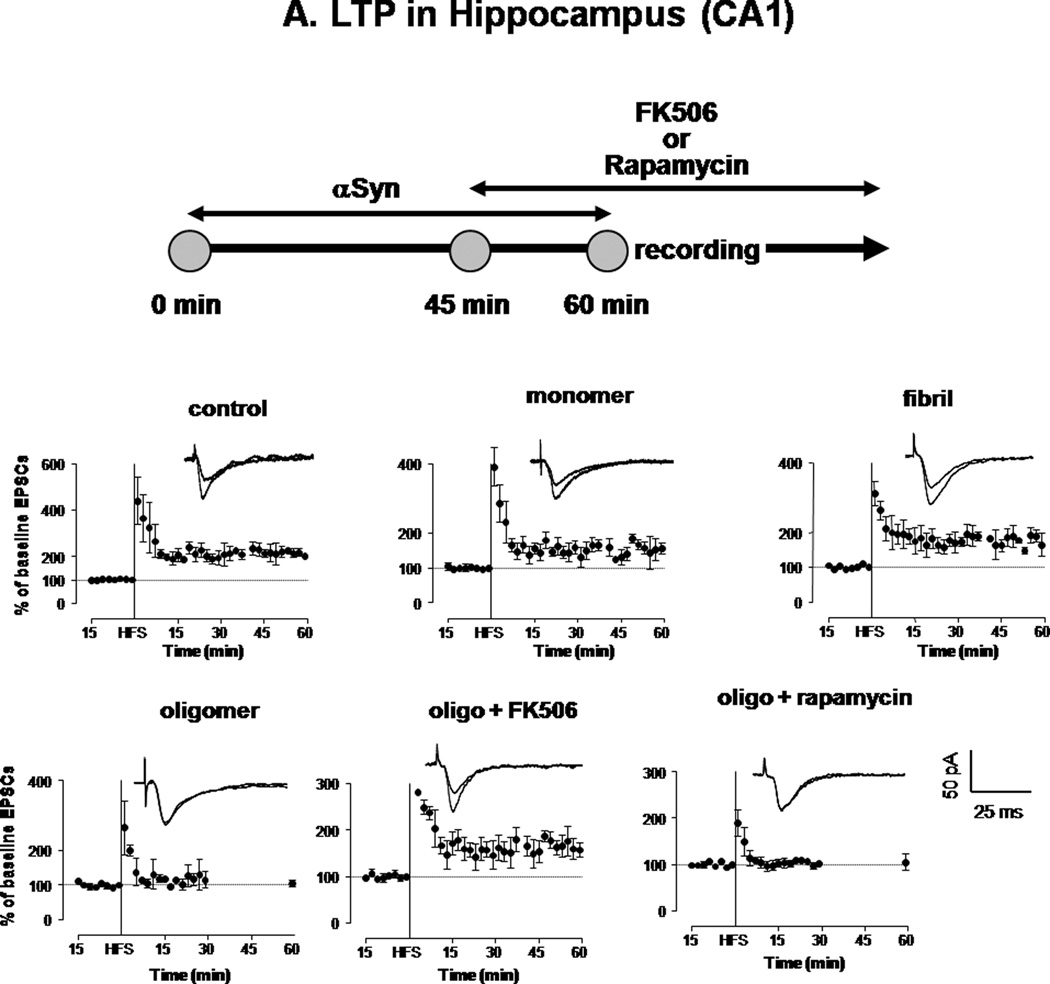
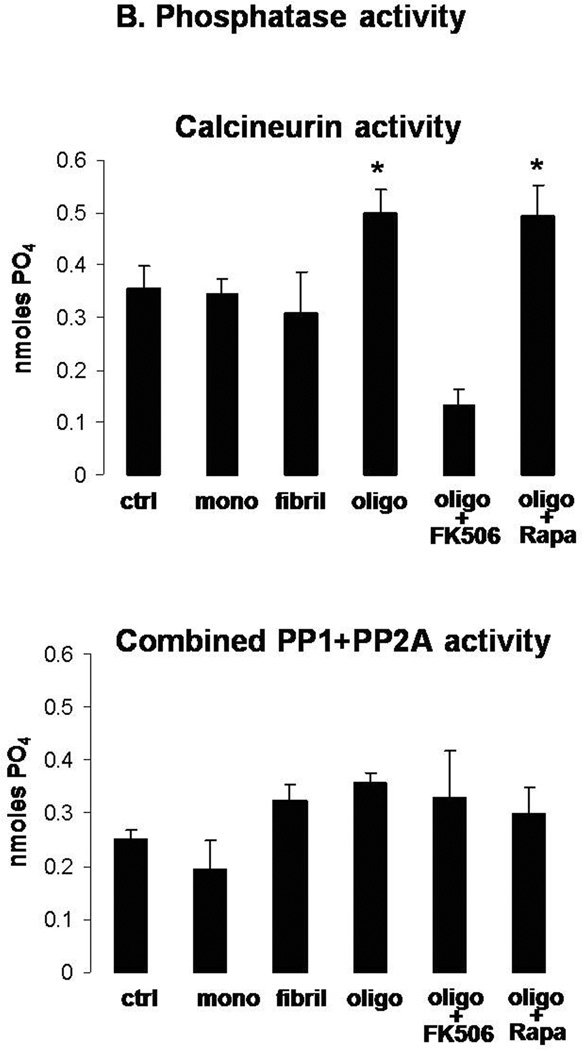
Figure 5. Oligomeric αSyn decreases LTP expression in hippocampal neurons in a CaN-dependent fashion.
A. HFS-induced expression of LTP in the hippocampus (CA1) of rat brain slices treated for 1 h with vehicle (control) or with 0.5 µM monomeric, oligomeric or fibrillar αSyn. A parallel set of oligomer-treated slices were additionally treated (45 min after addition of αSyn) with FK506 (10 µM) or rapamycin (10 µM), which remained in the perfusion buffer throughout the recording. Each symbol is the average of 10 monosynaptic EPSCs. Peak amplitudes were measured and expressed as percent of baseline values before HFS. Individual traces in inserts show averaged EPSCs recorded before and 30 min after HFS. Monosynaptic EPSCs were evoked by electrical stimulation (200 µs square-wave pulses at 0.033 Hz) of the Schaffer collateral/commissural pathway. LTP was evoked by 3 high-frequency trains (100 Hz, 1 s duration each; intertrain-interval 20 s). For illustration purposes, all scales were set to a maximum of 400 %.
B. CaN (top) and PP1+PP2A combined activity (bottom) assayed in the same brain slices shown in A at the end of the LTP recording. Columns represent mean ± S.D.; n=3 per group; *: p<0.05 vs. control (ANOVA).