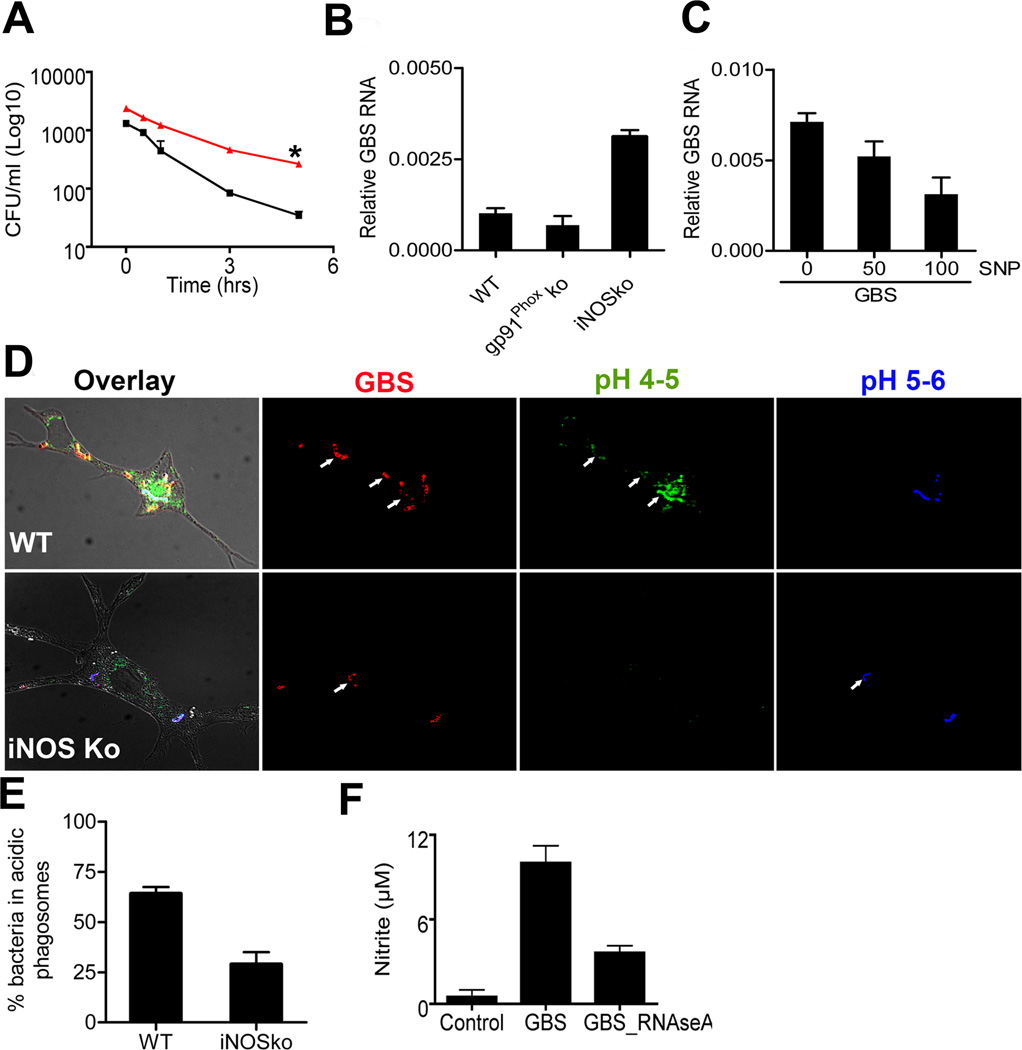
Fig. 4. iNOS is essential for the processing of nucleic acids from group B streptococcus.
A. WT BMDM (black) and BMDM lacking iNOS (red) were incubated with GBS (MOI 5), bacterial killing was measured and expressed as the bacteria surviving (CFU/ml) after different time intervals up to 5h. Statistical significance: P-value *<0. 05 B. Quantitative PCR of amplifiable GBS RNA was measured 24 h after stimulated with GBS (106/ml) in BMDM lacking gp91Phox or iNOS. C. Quantitative PCR of amplifiable GBS RNA measured 24 h after stimulation with the indicated concentrations of SNP (µM) in iNOSKo BMDM. D. Phagosomes of WT and iNOSko BMDM were loaded with the pH sensitive stain LysoSensor and stimulated with WGA-TRITC-labeled GBS (106/ml). Blue fluorescence indicates pH 5 - pH 6, whereas green fluorescence indicates more acidic environments. % GBS in acidic phagosome were measured by confocal microscopic analysis in BMDM lacking iNOS gene and WT. E. Quantitative analysis of GBS in phagosomes < pH5. F. BMDM from WT mice were stimulated with GBS (107/ml), which had been depleted or not for ssRNA by RNAseA enzymatic treatment. After 24 h, NO in the supernatant was determined. All the data is mean ± SD.