Figure 2.
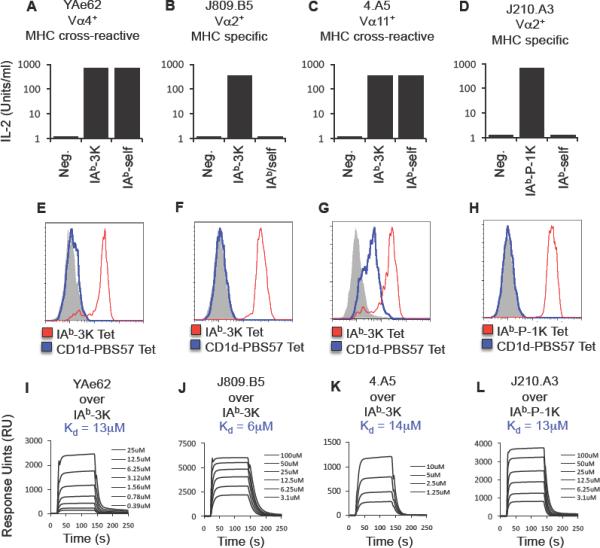
MHC cross-reactive TCRs are self-reactive, have different MHC cross-reactivities, yet have overlapping TCR-pMHC equilibrium affinities with MHC specific TCRs.
(A–D) The IAb-3K reactive T cell hybridomas (A) YAe62, (B) 4.A5 (isolated from an MHC CL2null mouse) and (C) J809.B5 (isolated from an MHCwt mouse) and the (D) IAb-P-1K-reactive T cell hybridoma J210.A3 (isolated from an MHCwt mouse) were stimulated with either antigen presenting cells (APC) expressing no MHC, IAb presenting 3K or P-1K, or IAb presenting endogenous self peptides. Data are average of triplicate wells and are representative of two experiments.
(E–H) The (E) YAe62, (F) 4.A5, (G) J809.B5 or (H) J210.A3 TCRs were expressed on the surface in SF9 cells and stained with IAb-3K or IAb-P-1K tetramer, and CD1d-PBS57 tetramer. Shaded histogram is a negative control tetramer. Data are representative example of three independent experiments.
(I–L) Soluble (I) YAe62, (J) 4.A5, (K) J809.B5 or (L) J210.A3 TCRs were analyzed for equilibrium binding to immobilized IAb-3K or IAb-P-1K using SPR. Sensograms are representative of two independent analyses.
