Figure 5.
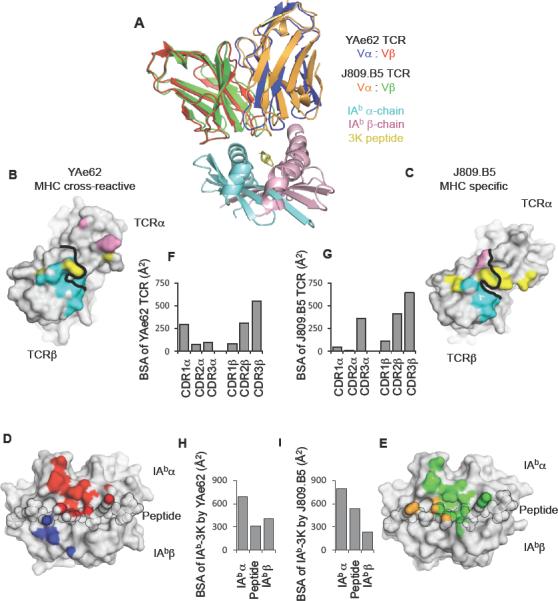
MHC cross-reactive and MHC specific TCRs bind IAb-3K within a similar footprint.
(A) Overlay of YAe62 and J809.B5 TCRs binding IAb-3K. The YAe62 TCR is colored red (TCRβ) and blue (TCRα); the J809.B5 TCR is colored green (TCRβ) and orange (TCRα). IAb-3K is colored cyan (IAbα chain), yellow (peptide) and magenta (IAbβ chain).
(B, C) Projection of IAb-3K binding onto the (B) YAe62 TCR, or (C) J809.B5 TCR. Contacts with the IAbα chain (colored cyan), peptide (colored yellow) and the IAbβ chain (colored magenta). Black line demarcates border of the TCRα subunit from the TCRβ subunit.
(D, E) Projection of the (D) YAe62 TCR or (E) J809.B5 TCR binding onto IAb-3K. YAe62 TCRα contacts are colored blue, YAe62 TCRβ contacts are colored red. The J809.B5 TCRα contacts are colored orange and the TCRβ contacts are colored yellow. The peptide residues are outlined in black.
(F–I) The amount of Buried Surface Area (BSA) contributed by the (F) YAe62 or (G) J809.B5 TCRα and TCRβ loops to the binding reaction with IAb-3K. (H) The amount of BSA contributed by the peptide or MHC chains for the binding reaction with YAe62 TCR or the (I) J809.B5 TCR. Figures were made using PyMol (DeLano).
