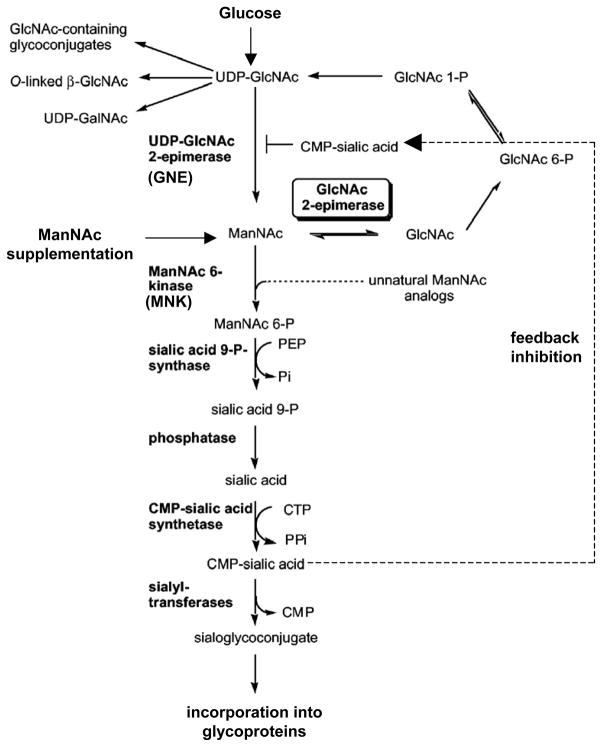
Figure 5.
Brief schematic representation of the sialic acid biosynthesis pathway. Glucose is converted into uridine diphosphate–N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) through a number of enzymatic steps (not shown), which is converted to N-acetyl-D-mannosamine (ManNAc) via a rate-limiting reaction calalyzed by GNE. ManNAc undergoes conversion to cytidine monophosphate–sialic acid (CMP-sialic acid), which provides feedback inhibition to the rate-limiting GNE-calalyzed reaction. Exogenous ManNAc supplements enters the pathway after this rate limiting step. A substantial part of the sialic acid is incorporated into N- and O-linked glycan residues in structural and secreted glycoproteins. Modified from Luchansky et al19 with permission of The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.