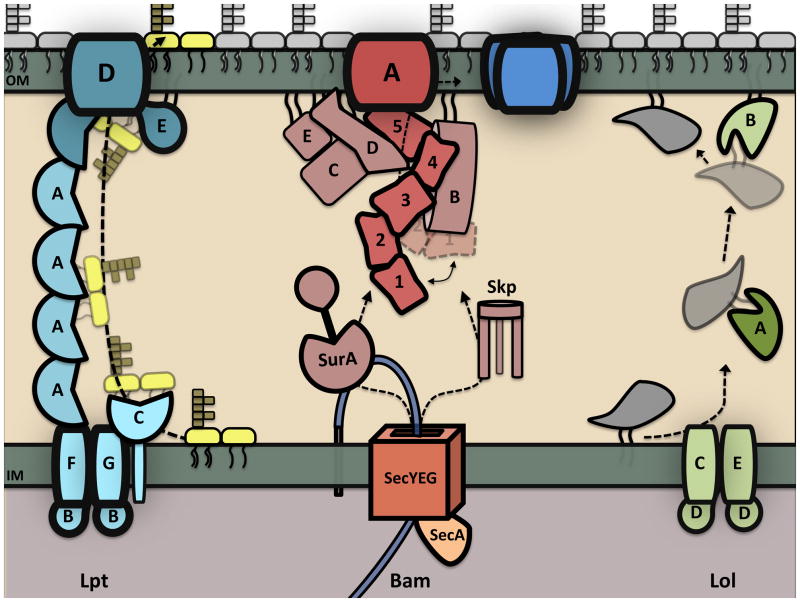
Figure 3.
OM biogenesis in E. coli. All components of the bacterial OM are synthesized in the cytoplasm and translocated across the IM into the periplasmic space. Once in the periplasm, each OM constituent traverses the envelope and integrates into the OM via a dedicated transport system (shown above). The Lpt components form a transenvelope protein bridge that shields the lipid A moiety from the aqueous environment and funnels LPS through LptDE to the cell surface. OM β-barrels (OMPs) cross the IM through the Sec translocon and associate with periplasmic chaperones that target OMPs to the Bam machine for assembly. OM lipoproteins are extracted from the IM in an ATP-dependent fashion and transferred to an OM receptor (LolB) via a periplasmic carrier protein (LolA). Phospholipid transport is not shown, as the mechanism by which they are trafficked to the OM is not known.