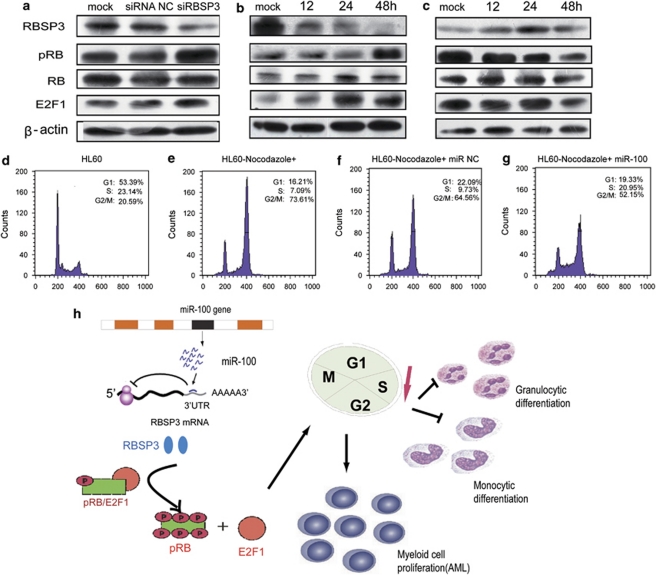
Figure 5.
MiR-100 targets RBSP3, which modulates the cell cycle effectors pRB/E2F1 and is involved in myeloid cell differentiation and proliferation. (a) RBSP3 knockdown promoted the phosphorylation of Rb and E2F1. After 72 h transfection with siRNA NC or siRBSP3, cells were collected to analyze the expression of RBSP3, pRb (phosphorylated Rb), Rb (total Rb protein) and E2F1 by western blotting using β-actin as an internal control. (b) MiR-100 overexpression induced the expression of pRB and E2F1 by downregulating RBSP3. The cells were collected at the indicated time points for western blot analysis. (c) The knockdown of miR-100 expression results in an upregulation of RBSP3 expression and a downregulation of pRB and E2F1 expression. Cells were collected at the indicated time points after transfection with miRNA antisense. Protein expression was assessed by western blot analysis. pRb, phosphorylated Rb; Rb, total Rb protein; β-actin, internal control. (d–g) MiR-100 promoted entry into S-phase of the cell cycle. (d) The cell cycle phase was analyzed by FACS at 24 h after the transfection with H2O in HL60 cells (without nocodazole). (e–g) Cell cycle phase data in HL60 cells transfected with H2O, miR-NC or miR-100 (with nocodazole). The data correspond to the mean of three independent experiments (P<0.05). (h) Schematic representation of a pathway modulated by miR-100 in myeloid cells undergoing differentiation toward granulocytosis/monocytosis and proliferation in AML. MiR-100 overexpression in myeloid cells induced progression through the G1/S transition and promoted S-phase entry. Thus, miR-100 induced cell proliferation and blocked promyeloid differentiation by repressing its downstream target RBSP3, which in turn resulted in the phosphorylation of RB and an accumulation of the downstream cell cycle effector E2F1.