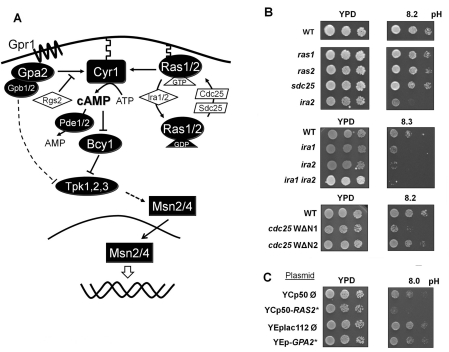
Figure 1. Effect of mutations in the upstream components of the PKA pathway on alkaline pH tolerance.
(A) A simplified schematic depiction of the PKA signalling pathway. See the Introduction section for additional information. (B) Upper panels: three dilutions of cultures of wild-type BY4741 cells and the isogenic kanMX disruption derivatives ras1, ras2, sds25 and ira2 mutants were spotted on to YPD plates adjusted at the indicated pH values. Middle panels: wild-type strains W303-1A and its ira1::LEU2 (strain SC7), ira2::URA3 (SC8) and ira1::LEU2 ira2::URA3 (PM903) derivatives were spotted as above. Lower panels: wild-type strains W303-1A and isogenic cells expressing the WΔN1 or WΔN2 alleles of CDC25 were spotted. All plates were incubated for 3 days. (C) Wild-type strain W303-1A was transformed with the indicated plasmids. Positive clones were grown overnight in synthetic selective medium and spotted on to YPD plates adjusted at the indicated pH and growth was monitored after 2 days. YCp50-RAS2* expresses a hyperactive allele (Ras2Ala18Val19) of the Ras protein. YEp-GPA2* generates a constitutively active Gpa2R273A version of the protein.