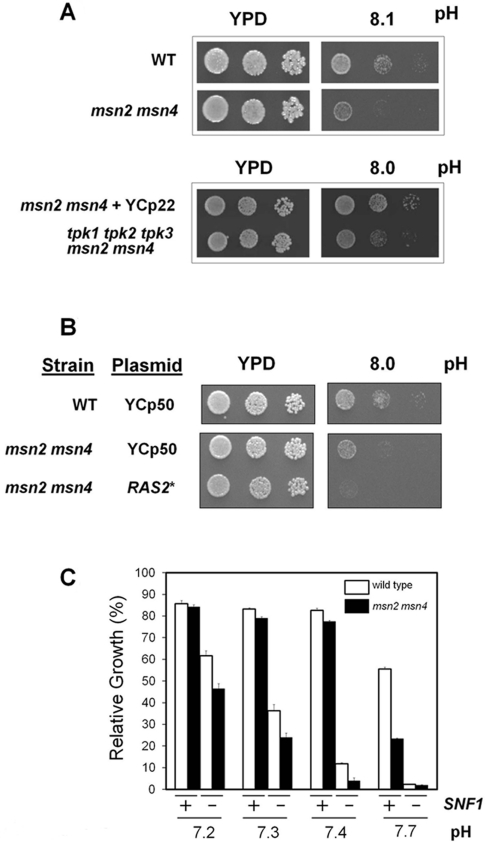
Figure 4. Effect of the lack of Msn2 and Msn4 transcription factors on high pH tolerance.
(A) Upper panels: wild-type W303-1A alone (WT) was plated along with strain MCY5278, a W303-1A-derived strain lacking both MSN2 and MSN4 genes. Lower panels: the MCY5278 strain was transformed with centromeric plasmid YCp22 (which carries a TRP1 gene marker, see the main text for an explanation) and plated with the equivalent strain but lacking all three TPK genes [14]. Dilutions of the cultures were grown for 2 days at the indicated pH. (B) The W303-1A strain (WT) and the msn2 msn4 derivative transformed with the empty plasmid YCp50 or the same plasmid carrying a hyperactive RAS2Ala18Val19 allele (RAS2*). Dilutions of the cultures were spotted on to YPD plates at the indicated pH values and growth was monitored after 2 days. (C) The W303-1A strain (open bars) and its msn2 msn4 derivative (closed bars) carrying a wild-type allele of SNF1 (+) or a snf1 deletion (−) were grown at the indicated pH values. Growth is denoted as the percentage compared with the same strains cultured at pH 5.5. Results are means±S.E.M. from two independent experiments performed in triplicate.