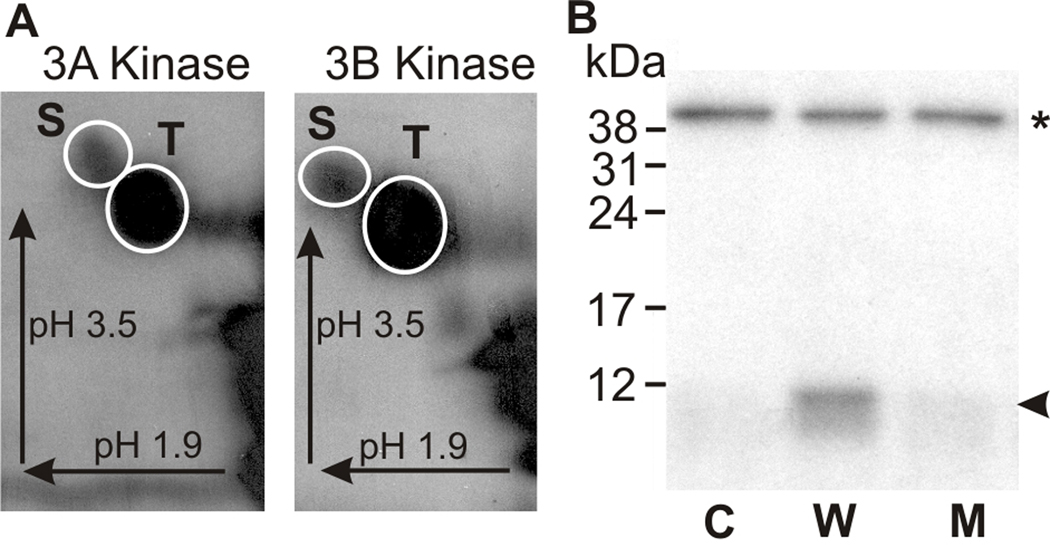
Figure 3. The kinase activation region of mMyo3B is phosphorylated by mMyo3A and 3B kinase on both serine and threonine residues.
The kinase activation region of mMyo3B used as substrate in these assays is indicated below the blue line in Figure 1. The polypeptide was expressed in E. coli and thus not post-translationally modified during expression. A. Phosphorimages of phosphorylated amino acids released from the mMyo3B kinase activation region phosphorylated by mMyo3A or 3B kinase as indicated. Incubations contained 10 µmol/Lsubstrate and 2.5 µmol/L kinase and continued for 1hr. Phosphorylated amino acids were separated in two dimensions by high voltage thin layer electrophoresis as described in the legend to Figure 2. Arrows indicate the directions of electrophoretic migration. White circles show locations of the phosphoserine (S) and phosphothreonine (T) amino acid standards. Both serines and threonines were phosphorylated. B. Autoradiograph of an SDS-PAGE gel examining the phosphorylation of the wild-type and mutated kinase activation region of mMyo3B by the full length mMyo3B kinase domain. Incubations contained 6µmol/L substrate and 0.15 µmol/L kinase. The full length kinase domain migrates at about 40 kDa (asterisk); the kinase activation region migrates at about 10 kDa (arrowhead). The full length kinase domain was incubated with no substrate (C, control), with the wild-type sequence of the kinase activation region (W); and with a mutated kinase activation region (M) in which the two phosphorylated residues identified by mass spectrometry, S171 and T178, were converted to alanines. The incubation in B was for 5 min.